Data Consistent Deep Rigid MRI Motion Correction
- PMID: 39415845
- PMCID: PMC11482239
Data Consistent Deep Rigid MRI Motion Correction
Abstract
Motion artifacts are a pervasive problem in MRI, leading to misdiagnosis or mischaracterization in population-level imaging studies. Current retrospective rigid intra-slice motion correction techniques jointly optimize estimates of the image and the motion parameters. In this paper, we use a deep network to reduce the joint image-motion parameter search to a search over rigid motion parameters alone. Our network produces a reconstruction as a function of two inputs: corrupted k-space data and motion parameters. We train the network using simulated, motion-corrupted k-space data generated with known motion parameters. At test-time, we estimate unknown motion parameters by minimizing a data consistency loss between the motion parameters, the network-based image reconstruction given those parameters, and the acquired measurements. Intra-slice motion correction experiments on simulated and realistic 2D fast spin echo brain MRI achieve high reconstruction fidelity while providing the benefits of explicit data consistency optimization. Our code is publicly available at https://www.github.com/nalinimsingh/neuroMoCo.
Figures
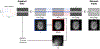
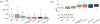
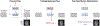
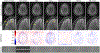
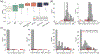
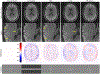
References
-
- Andre Jalal B, Bresnahan Brian W, Mossa-Basha Mahmud, Hoff Michael N, Smith C Patrick, Anzai Yoshimi, and Cohen Wendy A. Toward quantifying the prevalence, severity, and cost associated with patient motion during clinical MR examinations. Journal of the American College of Radiology, 12(7):689–695, 2015. - PubMed
-
- Batchelor PG, Atkinson D, Irarrazaval P, Hill DLG, Hajnal J, and Larkman D. Matrix description of general motion correction applied to multishot images. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 54(5):1273–1280, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Brau Anja CS, Beatty Philip J, Skare Stefan, and Bammer Roland. Comparison of reconstruction accuracy and efficiency among autocalibrating data-driven parallel imaging methods. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 59(2):382–395, 2008. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cordero-Grande Lucilio, Teixeira Rui Pedro AG, Hughes Emer J, Hutter Jana, Price Anthony N, and Hajnal Joseph V. Sensitivity encoding for aligned multishot magnetic resonance reconstruction. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2(3):266–280, 2016.
Grants and funding
- R21 EB018907/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB029641/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG070988/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 MH123195/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS105820/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB032708/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB017337/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB019956/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG068261/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG064027/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD087211/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB030006/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB003000/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH093765/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS070963/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS086625/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG064027/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG016495/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS052585/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 MH121885/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 EB001680/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB023281/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HD101553/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U24 NS100591/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG008122/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH117023/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS072652/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB015902/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB006758/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB015896/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS083534/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
