Lipoprotein subfractions of runners and sedentary men
- PMID: 3941608
- PMCID: PMC2824767
- DOI: 10.1016/0026-0495(86)90094-6
Lipoprotein subfractions of runners and sedentary men
Abstract
Serum concentrations of lipoprotein mass by flotation rate were measured in 12 long-distance runners and 64 sedentary men by analytic ultracentrifugation. The runners had significantly lower serum mass concentrations of the smaller, denser low-density lipoprotein particles of flotation rates Sf 0-7 (including the LDL-II, LDL-III, and LDL-IV subspecies), very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) particles of Sf 20-400, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles of flotation rates F1.20 0-1.5 (predominantly the HDL3 subspecies), and higher serum mass concentrations of HDL particles with flotation rates between F1.20 2.0-9.0 (including HDL2a and HDL2b and less dense particles belonging to HDL3) than did sedentary men. Lipoprotein lipase activity was higher, and hepatic lipase activity was lower in runners than in the sedentary men. Thus, the effects of endurance exercise training to lower LDL may be specific to the smaller, denser LDL particle region. Similarities in the lipoprotein mass profiles of the runners and the low-risk profiles of sedentary, middle-aged women suggest the effects of common metabolic factors possibly leading to reduced risk of coronary artery disease.
Figures
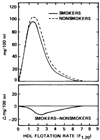

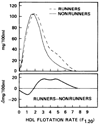
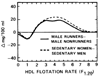

References
-
- Thompson P, Lazarus B, Cullinane E, et al. Exercise, diet. or physical characteristics as determinants of HDL-levels in endurance athletes. Atherosclerosis. 1983;46:333–339. - PubMed
-
- Huttunen JK, Lansimies E, Voutilainen E, et al. Effects of moderate physical activity on serum lipids. Circulation. 1979;60:1220–1229. - PubMed
-
- Lopez SA, Vial R, Balart L, et al. Effect of exercise and physical fitness on serum lipids and lipoproteins. Atherosclerosis. 1974;20:l–9. - PubMed
-
- Wood PD, Williams PT, Haskell WL. Physical activity and high-density lipoproteins. In: Miller NE, Miller GW, editors. Clinical and Metabolic Aspects of High-Density Lipoproteins. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1984. pp. 133–165.
-
- Wood PD, Haskell WL, Blair SN, et al. Increased exercise level and plasma lipoprotein concentrations: a one-year randomized study in sedentary middle-aged men. Metabolism. 1983;32:31–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

