This is a preprint.
Allele-specific silencing of a dominant SETX mutation in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis type 4
- PMID: 39416141
- PMCID: PMC11483056
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.10.11.617871
Allele-specific silencing of a dominant SETX mutation in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis type 4
Update in
-
Allele-specific silencing of a dominant SETX mutation in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis type 4.HGG Adv. 2025 Jul 10;6(3):100435. doi: 10.1016/j.xhgg.2025.100435. Epub 2025 Apr 8. HGG Adv. 2025. PMID: 40200577 Free PMC article.
Abstract
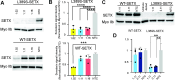
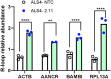
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 4 (ALS4) is an autosomal dominant motor neuron disease that is molecularly characterized by reduced R-loop levels and caused by pathogenic variants in senataxin (SETX). SETX encodes an RNA/DNA helicase that resolves three-stranded nucleic acid structures called R-loops. Currently, there are no disease-modifying therapies available for ALS4. Given that SETX is haplosufficient, removing the product of the mutated allele presents a potential therapeutic strategy. We designed a series of siRNAs to selectively target the RNA transcript from the ALS4 allele containing the c.1166T>C mutation (p.Leu389Ser). Transfection of HEK293 cells with siRNA and plasmids encoding either wild-type or mutant (Leu389Ser) epitope tagged SETX revealed that three siRNAs specifically reduced mutant SETX protein levels without affecting the wild-type SETX protein. In ALS4 primary fibroblasts, siRNA treatment silenced the endogenous mutant SETX allele, while sparing the wild-type allele, and restored R-loop levels in patient cells. Our findings demonstrate that mutant SETX, differing from wild-type by a single nucleotide, can be effectively and specifically silenced by RNA interference, highlighting the potential of allele-specific siRNA as a therapeutic approach for ALS4.
Keywords: R-loop; allele-specific silencing; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS); motor neuron; neurodegeneration; oligonucleotide therapeutics; senataxin; siRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATIONS OF INTEREST The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Rabin B.A., Griffin J.W., Crain B.J., Scavina M., Chance P.F., Cornblath D.R. (1999). Autosomal dominant juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 122, 1539–1550. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y-Z., Bennett C.L., Huynh H.M., Blair I.P., Puls I., Irobi J., Dierick I., Abel A., Kennerson M.L., Rabin B.A., Nicholson G.A., Auer-Grumbach M., Wagner K., De Jonghe P., Griffin J.W., Fischbeck K.H., Timmerman V., Cornblath D.R., Chance P.F. (2004). DNA/RNA helicase gene mutations in a form of juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS4). Am. J. Hum. Genet. 74, 1128–1135. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
