Isolated IgG4-related Infundibulo-hypophysitis
- PMID: 39416274
- PMCID: PMC11482006
- DOI: 10.1210/jcemcr/luae182
Isolated IgG4-related Infundibulo-hypophysitis
Abstract
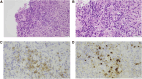
A 72-year-old man presented with several months of weakness, poor appetite, and depressed moods. Laboratory tests indicated central hypocortisolism, hypothyroidism and hypogonadism, and mild hyperprolactinemia. Imaging indicated a homogenously enhancing solid suprasellar mass inseparable from the hypothalamus and contiguous with a thickened proximal infundibulum. Neuro-ophthalmological evaluation was normal. Symptoms improved with hydrocortisone, levothyroxine, and testosterone replacement. After 6 months, transsphenoidal biopsy was performed due to mass enlargement and revealed fibrosis, lymphoplasmacytic infiltration, and CD138 and IgG4 staining. The levels of serum IgG4, complement, inflammatory markers, protein electrophoresis, amylase, and lipase and imaging of the chest, abdomen, and thyroid were unremarkable. After 1 month of prednisone therapy (starting dose 40 mg/day), the mass significantly involuted and remained stable afterward. Prednisone was gradually tapered to 5 mg daily over 10 weeks. During 22 months of follow-up, no systemic IgG4 disease was detected. Glucocorticoid, thyroid, and testosterone replacement was continued. This case of isolated IgG4-related hypophysitis illustrates the variable presentation that may not entail vasopressin deficiency or clinical mass effect. This entity should be considered in the differential diagnosis of suprasellar masses even in the absence of IgG4 systemic disease or characteristic serology. Management entails multidisciplinary collaboration and long-term follow-up.
Keywords: IgG4 disease; hypophysitis; hypopituitarism; pituitary mass.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures

References
-
- Kamisawa T, Zen Y, Pillai S, Stone JH. IgG4-related disease. Lancet. 2015;385(9976):1460‐1471. - PubMed
-
- Pinheiro FAG, Pereira IA, de Souza AWS, Giardini HAM, Cordeiro RA. IgG4-related disease—rare but you should not forget it. Adv Rheumatol. 2024;64(1):35. - PubMed
-
- Wallace ZS, Miles G, Smolkina E, et al. Incidence, prevalence and mortality of IgG4-related disease in the USA: a claims-based analysis of commercially insured adults. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023;82(7):957‐962. - PubMed
-
- Zhang W, Stone JH. Management of IgG4-related disease. Lancet Rheumatol. 2019;1(1):e55‐e65. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
