"Therapeutic advancements in nanomedicine: The multifaceted roles of silver nanoparticles"
- PMID: 39416696
- PMCID: PMC11446369
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biotno.2024.05.002
"Therapeutic advancements in nanomedicine: The multifaceted roles of silver nanoparticles"
Abstract
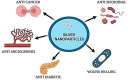
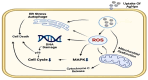
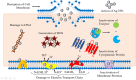
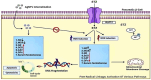
Nanotechnology has the advantages of enhanced bioactivity, reduced toxicity, target specificity, and sustained release and NPs can penetrate cell membranes. The small size of silver nanoparticles, AgNPs, large surface area, and unique physicochemical properties contribute to cell lysis and increased permeability of cell membranes used in the field of biomedicine. Functional precursors integrate with phytochemicals to create distinctive therapeutic properties and the stability of the nanoparticles can be enhanced by Surface coatings and encapsulation methods, The current study explores the various synthesis methods and characterization techniques of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and highlights their intrinsic activity in therapeutic applications, Anti-cancer activity noted at a concentration range of 5-50 μg/ml and angiogenesis is mitigated at a dosage range of 10-50 μg/ml, Diabetes is controlled within the same concentration. Wound healing is improved at concentrations of 10-50 μg/ml and with a typical range of 10-08 μg/ml for bacteria with antimicrobial capabilities. Advancement of silver nanoparticles with a focus on the future use of AgNPs-coated wound dressings and medical devices to decrease the risk of infection. Chemotherapeutic drugs can be administered by AgNPs, which reduces adverse effects and an improvement in treatment outcomes. AgNPs have been found to improve cell proliferation and differentiation, making them beneficial for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Our study highlights emerging patterns and developments in the field of medicine, inferring potential future paths.
Keywords: AgNps; Anti-inflammation; Anticancer; Biomedical applications; Nanotechnology; Reactive oxygen species.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Author do not have any Conflict of Interest.
Figures



References
-
- Malik M., Aamir Iqbal M., Iqbal Y., et al. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles for biomedical applications: a mini review. Inorg Chem Commun. 2022;145
-
- Shanmuganathan R., Karuppusamy I., Saravanan M., et al. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their biomedical applications - a comprehensive review. Curr Pharmaceut Des. 2019;25(24) - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

