[Surgical treatment of trigeminal pain]
- PMID: 39417851
- PMCID: PMC11576773
- DOI: 10.1007/s00482-024-00835-9
[Surgical treatment of trigeminal pain]
Abstract
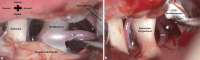
Surgical procedures for treating neuropathic pain, including trigeminal neuralgia (TGN), are categorized into three groups: decompression, ablation, and neuromodulation. Microvascular decompression is the only causal therapy for TGN, applicable favorably in cases of classical TGN due to a vascular nerve conflict. Ablative procedures include both percutaneous and radiosurgical methods, which are mainly used for idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. For irreversible neuropathies of the trigeminal nerve, the algorithm for other neuropathic pain conditions should be considered, along with the potential use of neuromodulatory techniques. When selecting a therapy, diagnosis, medication side effects, individual patient risks, and treatment outcomes must all be taken into account (current S1 guideline from the German Society of Neurology).
Die Schmerzchirurgie zur Behandlung von neuropathischen Schmerzen, zu denen auch die Trigeminusneuralgie (TGN) gehört, wird in die drei Gruppen der Dekompression, Ablation und Neuromodulation eingeteilt. Die Mikrovaskuläre Dekompression (MVD) ist die einzige kausale Therapie der TGN, die insbesondere im Falle der klassischen TGN auf Grund eines nachgewiesenen Gefäß-Nerven-Konflikts in Frage kommt. Zu den ablativen Verfahren gehören, neben den perkutanen, auch radiochirurgische Methoden, die vor allem bei der idiopathischen Trigeminusneuralgie zum Einsatz kommen. Bei irreversiblen Neuropathien des Nervus trigeminus gilt der Therapiealgorithmus anderer neuropathischer Schmerzen und gegebenenfalls der Einsatz neuromodulativer Verfahren. Für die Auswahl der Therapie müssen die Diagnose, die Nebenwirkungen der Medikamente und die individuellen Risiken der Patienten neben den Behandlungsergebnissen berücksichtigt werden (siehe aktuelle S1 Leitlinie der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Neurologie).
Keywords: Microvascular decompression; Neuromodulation; Neuropathic facial pain; Radiosurgery; Thermocoagulation.
© 2024. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) (2018) The International Classification of Headache Disorders. Cephalalgia 38:1–211 (3rd edition) - PubMed
-
- Ruscheweyh R, Gierthmühlen J, Hedderich DM et al (2024) Medikamentöse Therapie der Trigeminusneuralgie. Schmerz 38:283–292 - PubMed
-
- Mueller D, Obermann M, Yoon MS et al (2011) Prevalence of trigeminal neuralgia and persistent idiopathic facial pain: a population-based study. Cephalalgia 31:1542–1548 - PubMed
-
- Thomas KL, Vilensky JA (2014) The anatomy of vascular compression in trigeminal neuralgia. Clin Anat 27:89–93 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

