Influence of Microenvironmental Orchestration on Multicellular Lung Alveolar Organoid Development from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
- PMID: 39417930
- PMCID: PMC11762634
- DOI: 10.1007/s12015-024-10789-1
Influence of Microenvironmental Orchestration on Multicellular Lung Alveolar Organoid Development from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Abstract
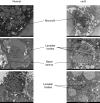
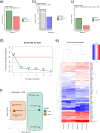
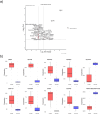
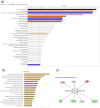
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have emerged as promising in vitro tools, providing a robust system for disease modelling and facilitating drug screening. Human iPSCs have been successfully differentiated into lung cells and three-dimensional lung spheroids or organoids. The lung is a multicellular complex organ that develops under the symphonic influence of the microenvironment. Here, we hypothesize that the generation of lung organoids in a controlled microenvironment (cmO) (oxygen and pressure) yields multicellular organoids with architectural complexity resembling the lung alveoli. iPSCs were differentiated into mature lung organoids following a stepwise protocol in an oxygen and pressure-controlled microenvironment. The organoids developed in the controlled microenvironment displayed complex alveolar architecture and stained for SFTPC, PDPN, and KRT5, indicating the presence of alveolar epithelial type II and type I cells, as well as basal cells. Moreover, gene and protein expression levels were also increased in the cmO. Furthermore, pathway analysis of proteomics revealed upregulation of lung development-specific pathways in the cmO compared to those growing in normal culture conditions. In summary, by using a controlled microenvironment, we established a complex multicellular lung organoid derived from iPSCs as a novel cellular model to study lung alveolar biology in both lung health and disease.
Keywords: 3D organoids; Induced pluripotent stem cells; Lung organoids; Lung proteomics; Multicellular lung organoid.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical Approval: Not applicable, no human or animal study performed. Consent to Participate: Not applicable. Consent to Publish: All authors agree to the publish the data. Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

