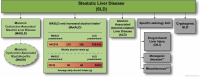
MASLD: What We Have Learned and Where We Need to Go-A Call to Action
- PMID: 39418184
- PMCID: PMC11580021
- DOI: 10.1148/rg.240048
MASLD: What We Have Learned and Where We Need to Go-A Call to Action
Abstract
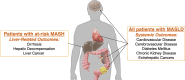
Since its introduction in 1980, fatty liver disease (now termed metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease [MASLD]) has grown in prevalence significantly, paralleling the rise of obesity worldwide. While MASLD has been the subject of extensive research leading to significant progress in the understanding of its pathophysiology and progression factors, several gaps in knowledge remain. In this pictorial review, the authors present the latest insights into MASLD, covering its recent nomenclature change, spectrum of disease, epidemiology, morbidity, and mortality. The authors also discuss current qualitative and quantitative imaging methods for assessing and monitoring MASLD. Last, they propose six unsolved challenges in MASLD assessment, which they term the proliferation, reproducibility, reporting, needle-in-the-haystack, availability, and knowledge problems. These challenges offer opportunities for the radiology community to proactively contribute to their resolution. The authors conclude with a call to action for the entire radiology community to claim a seat at the table, collaborate with other societies, and commit to advancing the development, validation, dissemination, and accessibility of the imaging technologies required to combat the looming health care crisis of MASLD.
© RSNA, 2024 See the invited commentary by Venkatesh in this issue.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

![History of MASLD literature. Graph shows the number of NAFLD (MASLD)
publications per year from 1980 to 2023. Those highlighted are the first
publication to describe NAFLD in 1980 (four authors from one institution) and
the consensus paper in 2023 announcing the new MASLD nomenclature (236
contributors from 56 countries and representing seven scientific societies).
(Embedded maps created with and adapted and reprinted under a CC BY-SA 4.0
license from MapChart [https://www.mapchart.net/].)](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/a08f/11580021/f728ee5eb00d/rg.240048.fig1.gif)
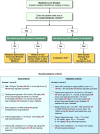
![MASLD spectrum. Conventional histologic images show steatosis with fat
droplets within hepatocytes (*), steatohepatitis with ballooned
hepatocytes (B), early-stage fibrotic liver with pericellular fibrosis
(black arrow), and cirrhotic liver with fibrotic scars (yellow arrow)
surrounding a regenerative nodule (N). MASL refers to steatosis without
inflammation or cell injury. MASH refers to steatosis with inflammation and
cell injury. Fibrosis refers to excess collagen deposition in the
extracellular matrix and is a marker of cumulative liver damage. Cirrhosis
is a late stage of disease in which fibrotic scars have carved the liver
into regenerative nodules. At-risk MASH is defined by the combination of
MASH, an NAFLD activity score of 4 or greater, and a fibrosis score of 2 or
greater. NAFLD activity score is the sum of the steatosis grade
(0–3), lobular inflammation grade (0–3), and ballooning score
(0–2). (Hematoxylin-eosin stain [two left images] and trichrome stain
[two right images].)](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/a08f/11580021/0fad64c9e2e0/rg.240048.fig4.gif)
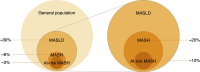
![MASLD prevalence worldwide. South and Central America has the highest
prevalence of MASLD (44%) and western Europe has the lowest (25%) (10). (Map
created with and adapted and reprinted under a CC BY-SA 4.0 license from
MapChart [https://www.mapchart.net/].)](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/a08f/11580021/01fd1ada4824/rg.240048.fig6.gif)
![MASLD estimated annual percentage change worldwide. The four areas
with the highest rate of increase are Oman (2.1%), Finland (1.7%),
Equatorial Guinea (1.7%), and Nicaragua (1.6%). There are no areas in which
the prevalence is decreasing. (Adapted and reprinted under a CC BY-NC 4.0
license from reference 11. Map created with and adapted and reprinted under
a CC BY-SA 4.0 license from MapChart
[https://www.mapchart.net/].)](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/a08f/11580021/7aded2937f13/rg.240048.fig7.gif)

![Proliferation problem. Word cloud illustration shows the
conglomeration of circulating- (orange), imaging- (black), and
“-omics”- (brown) based diagnostic tests currently available
for MASLD. In this figure, -omics refers to genomics, proteomics,
metabolomics, and lipidomics. Radiomics are considered imaging biomarkers
for the purpose of this figure. (Reprinted with permission from and
generated using Wordclouds.com [https://www.wordclouds.com/.])](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/a08f/11580021/e95732af7b3e/rg.240048.fig18.gif)
![Proportion of HCC attributable to MASLD worldwide. India has the
highest proportion of HCC attributable to MASLD (38%) and China has the
lowest (1%) (70). (Map created with and adapted and reprinted under a CC
BY-SA 4.0 license from MapChart [https://www.mapchart.net/].)](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/a08f/11580021/db5e8d449049/rg.240048.fig20.gif)





References
-
- Ludwig J , Viggiano TR , McGill DB , Oh BJ . Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease . Mayo Clin Proc 1980. ; 55 ( 7 ): 434 – 438 . - PubMed
-
- Eslam M , Sanyal AJ , George J ; International Consensus Panel . MAFLD: A Consensus-Driven Proposed Nomenclature for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease . Gastroenterology 2020. ; 158 ( 7 ): 1999 – 2014.e1 . - PubMed
-
- McPherson S , Hardy T , Henderson E , Burt AD , Day CP , Anstee QM . Evidence of NAFLD progression from steatosis to fibrosing-steatohepatitis using paired biopsies: implications for prognosis and clinical management . J Hepatol 2015. ; 62 ( 5 ): 1148 – 1155 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 DK130190/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK110096/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 FD007773/FD/FDA HHS/United States
- T32 EB005970/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK088925/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB029046/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA195443/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB032638/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061734/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA256708/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R43 DK135225/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA226528/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R43 EB034626/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD089935/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK106419/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

