Therapy concepts in type 1 diabetes mellitus treatment: disease modifying versus curative approaches
- PMID: 39420138
- PMCID: PMC11579207
- DOI: 10.1007/s00109-024-02494-w
Therapy concepts in type 1 diabetes mellitus treatment: disease modifying versus curative approaches
Abstract
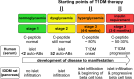
For many autoimmune diseases, including type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM), efforts have been made to modify the disease process through pharmacotherapy. The ultimate goal must be to develop therapies with curative potential by achieving an organ without signs of parenchymal cell destruction and without signs of immune cell infiltration. In the case of the pancreas, this means regenerated and well-preserved beta cells in the islets without activated infiltrating immune cells. Recent research has opened up the prospect of successful antibody combination therapy for autoimmune diabetes with curative potential. This goal cannot be achieved with monotherapies. The requirements for the implementation of such a therapy with curative potential for the benefit of patients with T1DM and LADA (latent autoimmune diabetes in adults) are considered.
Keywords: Autoimmune diseases; Disease modifying and curative therapies; Latent autoimmune diabetes in adults; Type 1 diabetes mellitus.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bliss M (1982) Glory enough for all. McClelland and Stewart, Toronto
-
- Chatzantoni K, Mouzaki A (2006) Anti-TNF-alpha antibody therapies in autoimmune diseases. Curr Top Med Chem 6:1707–1714 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

