Identification of tauopathy-associated lipid signatures in Alzheimer's disease mouse brain using label-free chemical imaging
- PMID: 39420210
- PMCID: PMC11487145
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-024-07034-3
Identification of tauopathy-associated lipid signatures in Alzheimer's disease mouse brain using label-free chemical imaging
Abstract
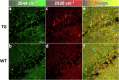
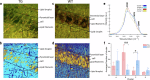
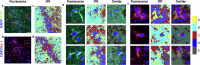
There is cumulative evidence that lipid metabolism plays a key role in the pathogenesis of various neurodegenerative disorders including Alzheimer's disease (AD). Visualising lipid content in a non-destructive label-free manner can aid in elucidating the AD phenotypes towards a better understanding of the disease. In this study, we combined multiple optical molecular-specific methods, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopic imaging, synchrotron radiation-infrared (SR-IR) microscopy, Raman and stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) microscopy, and optical-photothermal infrared (O-PTIR) microscopy with multivariate data analysis, to investigate the biochemistry of brain hippocampus in situ using a mouse model of tauopathy (rTg4510). We observed a significant difference in the morphology and lipid content between transgenic (TG) and wild type (WT) samples. Immunohistochemical staining revealed some degree of microglia co-localisation with elevated lipids in the brain. These results provide new evidence of tauopathy-related dysfunction in a preclinical study at a subcellular level.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In vivo reactive astrocyte imaging using [18F]SMBT-1 in tauopathy and familial Alzheimer's disease mouse models: A multi-tracer study.J Neurol Sci. 2024 Jul 15;462:123079. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2024.123079. Epub 2024 Jun 4. J Neurol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38878650
-
Detection of Aβ plaque-associated astrogliosis in Alzheimer's disease brain by spectroscopic imaging and immunohistochemistry.Analyst. 2018 Feb 12;143(4):850-857. doi: 10.1039/c7an01747b. Analyst. 2018. PMID: 29230441 Free PMC article.
-
A novel transgenic mouse expressing double mutant tau driven by its natural promoter exhibits tauopathy characteristics.Exp Neurol. 2008 Jul;212(1):71-84. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.03.007. Epub 2008 Mar 21. Exp Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18490011
-
Tau Seeding Mouse Models with Patient Brain-Derived Aggregates.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 7;22(11):6132. doi: 10.3390/ijms22116132. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34200180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglial Activation During Pathogenesis of Tauopathy in rTg4510 Mice: Implications for the Early Diagnosis of Tauopathy.J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;64(s1):S353-S359. doi: 10.3233/JAD-179933. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018. PMID: 29865054 Review.
Cited by
-
Strain-Distinct α-Synuclein and Tau Cross-Seeding Uncovered by Correlative Approach with Optical Photothermal Infrared Sub-Micron Imaging.J Am Chem Soc. 2025 Aug 6;147(31):27323-27340. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5c02811. Epub 2025 Jul 28. J Am Chem Soc. 2025. PMID: 40726080 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization, https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia (2023).
-
- Daroff, R. B. & Aminoff, M. J. Encyclopedia of The Neurological Sciences (Academic press, 2014).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

