Research progress of ankyrin repeat domain 1 protein: an updated review
- PMID: 39420247
- PMCID: PMC11488291
- DOI: 10.1186/s11658-024-00647-w
Research progress of ankyrin repeat domain 1 protein: an updated review
Abstract
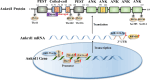
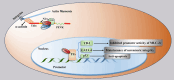
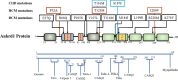
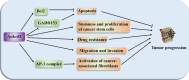
Ankyrin repeat domain 1 (Ankrd1) is an acute response protein that belongs to the muscle ankyrin repeat protein (MARP) family. Accumulating evidence has revealed that Ankrd1 plays a crucial role in a wide range of biological processes and diseases. This review consolidates current knowledge on Ankrd1's functions in myocardium and skeletal muscle development, neurogenesis, cancer, bone formation, angiogenesis, wound healing, fibrosis, apoptosis, inflammation, and infection. The comprehensive profile of Ankrd1 in cardiovascular diseases, myopathy, and its potential as a candidate prognostic and diagnostic biomarker are also discussed. In the future, more studies of Ankrd1 are warranted to clarify its role in diseases and assess its potential as a therapeutic target.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Ankrd1; Cardiovascular diseases; Skeletal muscle diseases; Tumor therapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ankyrin Repeat Domain 1 Protein: A Functionally Pleiotropic Protein with Cardiac Biomarker Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jun 26;18(7):1362. doi: 10.3390/ijms18071362. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28672880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel role for cardiac ankyrin repeat protein Ankrd1/CARP as a co-activator of the p53 tumor suppressor protein.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2010 Oct 1;502(1):60-7. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2010.06.029. Epub 2010 Jul 3. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2010. PMID: 20599664
-
The enigmatic role of the ankyrin repeat domain 1 gene in heart development and disease.Int J Dev Biol. 2008;52(7):811-21. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.082655am. Int J Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18956313 Review.
-
ANKRD1 aggravates renal ischaemia‒reperfusion injury via promoting TRIM25-mediated ubiquitination of ACSL3.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Sep;14(9):e70024. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70024. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39285846 Free PMC article.
-
ANKRD1 modulates inflammatory responses in C2C12 myoblasts through feedback inhibition of NF-κB signaling activity.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Aug 14;464(1):208-13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.06.118. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26102030
Cited by
-
Cytoskeletal signaling as a shared pathway for convergent genetic mechanisms underlying loss of flight in birds.Poult Sci. 2025 Jun 28;104(9):105503. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105503. Online ahead of print. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40592285 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Structural Variation Analysis and Breed Comparison of Local Domestic Ducks in Shandong Province, China.Animals (Basel). 2024 Dec 18;14(24):3657. doi: 10.3390/ani14243657. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39765561 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiology's best friend: Using naturally occurring disease in dogs to understand heart disease in humans.J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. 2025 Jul 4;13:100474. doi: 10.1016/j.jmccpl.2025.100474. eCollection 2025 Sep. J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. 2025. PMID: 40686503 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kojic S, Radojkovic D, Faulkner G. Muscle ankyrin repeat proteins: their role in striated muscle function in health and disease. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2011;48(5–6):269–94. - PubMed
-
- Chu W, Burns DK, Swerlick RA, Presky DH. Identification and characterization of a novel cytokine-inducible nuclear protein from human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(17):10236–45. - PubMed
-
- Jeyaseelan R, Poizat C, Baker RK, Abdishoo S, Isterabadi LB, Lyons GE, et al. A novel cardiac-restricted target for doxorubicin. CARP, a nuclear modulator of gene expression in cardiac progenitor cells and cardiomyocytes. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(36):22800–8. - PubMed
-
- Kuo H, Chen J, Ruiz-Lozano P, Zou Y, Nemer M, Chien KR. Control of segmental expression of the cardiac-restricted ankyrin repeat protein gene by distinct regulatory pathways in murine cardiogenesis. Development. 1999;126(19):4223–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

