Causal Inference for Continuous Multiple Time Point Interventions
- PMID: 39420673
- PMCID: PMC11586917
- DOI: 10.1002/sim.10246
Causal Inference for Continuous Multiple Time Point Interventions
Abstract
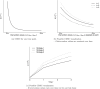
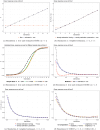
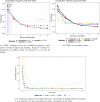
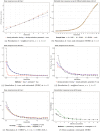
There are limited options to estimate the treatment effects of variables which are continuous and measured at multiple time points, particularly if the true dose-response curve should be estimated as closely as possible. However, these situations may be of relevance: in pharmacology, one may be interested in how outcomes of people living with-and treated for-HIV, such as viral failure, would vary for time-varying interventions such as different drug concentration trajectories. A challenge for doing causal inference with continuous interventions is that the positivity assumption is typically violated. To address positivity violations, we develop projection functions, which reweigh and redefine the estimand of interest based on functions of the conditional support for the respective interventions. With these functions, we obtain the desired dose-response curve in areas of enough support, and otherwise a meaningful estimand that does not require the positivity assumption. We develop -computation type plug-in estimators for this case. Those are contrasted with g-computation estimators which are applied to continuous interventions without specifically addressing positivity violations, which we propose to be presented with diagnostics. The ideas are illustrated with longitudinal data from HIV positive children treated with an efavirenz-based regimen as part of the CHAPAS-3 trial, which enrolled children years in Zambia/Uganda. Simulations show in which situations a standard g-computation approach is appropriate, and in which it leads to bias and how the proposed weighted estimation approach then recovers the alternative estimand of interest.
© 2024 The Author(s). Statistics in Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Robins J. M., Hernan M. A., and Brumback B., “Marginal Structural Models and Causal Inference in Epidemiology,” Epidemiology 11, no. 5 (2000): 550–560. - PubMed
-
- Robins J., “A New Approach to Causal Inference in Mortality Studies With a Sustained Exposure Period—Application to Control of the Healthy Worker Survivor Effect,” Mathematical Modelling 7, no. 9–12 (1986): 1393–1512.
-
- Bang H. and Robins J. M., “Doubly Robust Estimation in Missing Data and Causal Inference Models,” Biometrics 64, no. 2 (2005): 962–972. - PubMed
-
- Van der Laan M. and Rose S., Targeted Learning (New York: Springer, 2011).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
