Correlating tissue and plasma‑specific piRNA changes to predict their possible role in pancreatic malignancy and chronic inflammation
- PMID: 39420923
- PMCID: PMC11484194
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2024.1874
Correlating tissue and plasma‑specific piRNA changes to predict their possible role in pancreatic malignancy and chronic inflammation
Abstract
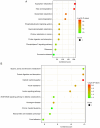
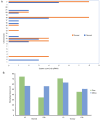
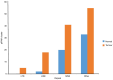
The aggressiveness of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is primarily due to lack of effective early detection biomarkers. Circulating non-coding RNAs serve as diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers in multiple types of cancer. Comparison of their expression between diseased tissue and relevant body fluids such as saliva, urine, bile, pancreatic juice, blood etc. may reveal mechanistic involvement of common non-coding RNAs. piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) are a class of non-coding RNAs. The aim of the present study was to investigate plasma and tumour tissue piRNA changes in patients with pancreatic cancer (PC) and explore the possible role in tumorigenesis and pancreatic inflammation. Sequencing of circulating plasma small RNAs from patients with PC and chronic pancreatitis (CP) was performed and differentially expressed piRNAs were compared with those in tissues. Subsequent search for target genes for those piRNAs was performed followed by pathway and cluster analysis. A total of 36 piRNAs were shown to be deregulated in pancreatic tumour tissue and alteration of 11 piRNAs was detected in plasma of patients with PC. piRNAs hsa-piR-23246, hsa-piR-32858 and hsa-piR-9137 may serve a key role in PC development as their expression was correlated in both plasma and tumour tissue. Key piRNA-target interactions interfering with key biological pathways were also characterized. A total of 19 deregulated piRNAs in plasma samples of patients with CP was identified; these targeted genes responsible for chronic inflammation. Therefore, the present study provides a comprehensive description of piRNA alteration in pancreatic malignancy and inflammation; these may be explored for biomarker potential in future.
Keywords: chronic pancreatitis; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; piRNA; plasma; tissue.
Copyright: © 2024 Saha et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PIWI-interacting RNAs are aberrantly expressed and may serve as novel biomarkers for diagnosis of lung adenocarcinoma.Thorac Cancer. 2021 Sep;12(18):2468-2477. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14094. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Thorac Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34346164 Free PMC article.
-
Testicular piRNA profile comparison between successful and unsuccessful micro-TESE retrieval in NOA patients.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2018 May;35(5):801-808. doi: 10.1007/s10815-018-1134-4. Epub 2018 Feb 19. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2018. PMID: 29460056 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profile analysis of piwi-interacting RNA in forensically relevant biological fluids.Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2019 Sep;42:171-180. doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2019.07.015. Epub 2019 Jul 25. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2019. PMID: 31369993
-
Piwi-Interacting RNAs: A New Class of Regulator in Human Breast Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 6;11:695077. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.695077. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34295823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PiWi RNA in Neurodevelopment and Neurodegenerative Disorders.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2022;15(3):517-531. doi: 10.2174/1874467214666210629164535. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34212832 Review.
Cited by
-
piRNAs as Potential Regulators of Mammary Gland Development and Pathology in Livestock.Vet Sci. 2025 Jun 17;12(6):594. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12060594. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40559831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of noncoding RNA and protein interaction in pancreatic cancer.Chin Med J (Engl). 2025 May 5;138(9):1019-1036. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003587. Epub 2025 Apr 10. Chin Med J (Engl). 2025. PMID: 40205638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Regulatory Noncoding RNAs in Human Cancer: The State of the Art in Clinical Trials.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Apr 4;17(4):471. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040471. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40284466 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
