Real world clinical outcomes from targeted intraoperative radiotherapy (TARGIT-IORT) during lumpectomy for breast cancer: data from a large cohort at a national cancer institute
- PMID: 39421443
- PMCID: PMC11484062
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1424630
Real world clinical outcomes from targeted intraoperative radiotherapy (TARGIT-IORT) during lumpectomy for breast cancer: data from a large cohort at a national cancer institute
Abstract
Introduction: Randomised evidence supports the use of partial breast irradiation (PBI) with targeted intraoperative radiotherapy (TARGIT-IORT) for early stage breast cancer, but prospective data from real-world adoption of this technique is also important. The aim of this study was to determine if the outcome reported in TARGIT-A trial could be replicated in large cohort of early stage breast cancer treated with TARGIT-IORT.
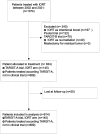
Methods: This prospective observational study analysed all patients treated with TARGIT-IORT between 2004 and 2021 in a single national cancer institute. TARGIT-IORT during lumpectomy was performed according to the risk-adapted TARGIT-A protocol using the Intrabeam® device. We analysed the completeness of follow up, 5-year in-breast-tumour-recurrence (IBTR), long term local recurrence free survival, distant disease-free survival, overall survival and breast-cancer-related survival, using the Kaplan-Meier method. A covariate analysis was performed to investigate risk factors for IBTR. We also analysed high grade toxicity events.
Results: The study included 814 patients and the a median follow up was 72 months. The majority of patients (60.3%) received TARGIT-IORT as PBI modality ("exclusive IORT" group); 39.7% received additional EBRT. There was no significant difference between the 5 years IBTR for the whole study population and the "exclusive IORT" cohort (1.6% (95%CI=1.1-2.1%) and 2.5% (95%CI=1.7%-3.3%) respectively). 5 years overall survival and tumour related survival were >95%. In 21% of patients with recurrence, breast was preserved. Radiotherapy toxicity (CTCAE Grade>2) was very rare (0.9%).
Conclusions: This large single institute study found that breast cancer control and survival outcomes with TARGIT-IORT were consistent with TARGIT-A trial results. This "real world" experience confirmed that the randomised evidence showing the value of TARGIT-IORT as partial breast irradiation modality that can be replicated in routine clinical practice.
Keywords: TARGIT-IORT; breast cancer; intraoperative radiotherapy; real world data; registry.
Copyright © 2024 Vinante, Vaidya, Caroli, Mileto, Piccoli, Avanzo, Barresi, Marson, Montico, Baboci, Perin, Urbani, Puglisi, Mascarin and Massarut.
Conflict of interest statement
JV: Research support from University College London Hospitals UCLH/UCL Comprehensive Biomedical Research Centre, UCLH Charities, National Institute for Health Research NIHR Health Technology Assessment HTA programme, Ninewells Cancer Campaign, National Health and Medical Research Council, German Federal Ministry of Education and Research BMBF, and Cancer Research Campaign now Cancer Research UK, Photoelectron Corp 1996-99, Carl Zeiss for supporting data management at the University of Dundee Dundee, UK, 2004-2008, and some conference expenses and honorariums. MA: consulting fee from L’Institut national de la santé et de la recherche médicale INSERM, France International Agency for Atomic Energy IAEA, Vienna International Centre for Theoretical Physics ICTP by Unesco and supporting grant from European Federation of Organizations for Medical Physics EFOMP Italian Association of Medical Physicists AIFM. FP: research grant/consulting fees/honoraria from Astrazeneca, Daichii Sandoz, Eli Lilly, Exact Science, Lidead. Menarini, MSD, Novartis Pfizer, Roche, Seagen. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

References
-
- Vaidya JS, Joseph DJ, Tobias JS, Bulsara M, Wenz F, Saunders C, et al. . Targeted intraoperative radiotherapy versus whole-breast radiotherapy for breast cancer (TARGIT-A trial): an international, prospective, randomised, non-inferiority phase 3 trial. Lancet. (2010) 376:91–102. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60837-9 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vaidya JS, Wenz F, Bulsara M, Tobias JS, Joseph DJ, Keshtgar M, et al. . Risk-adapted targeted intraoperative radiotherapy versus whole-breast radiotherapy for breast cancer: 5-year results for local control and overall survival from the TARGIT-A randomised trial. Lancet. (2014) 383:603–13. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61950-9 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vaidya JS, Bulsara M, Baum M, Wenz F, Massarut S, Pigorsch S, et al. . Long term survival and local control outcomes from single dose targeted intraoperative radiotherapy during lumpectomy (TARGIT-IORT) for early breast cancer: TARGIT-A randomised clinical trial. BMJ. (2020) 370:m2836. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m2836 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

