Expanding the VEXAS diagnostic workup: the role of peripheral blood cytological analysis
- PMID: 39421750
- PMCID: PMC11484077
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1466720
Expanding the VEXAS diagnostic workup: the role of peripheral blood cytological analysis
Abstract
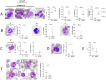
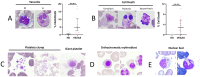
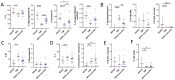
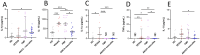
VEXAS syndrome is a newly described autoinflammatory entity characterized by somatic mutations in the UBA1 X-linked gene in hematopoietic progenitor cells. Several studies have demonstrated that the presence of vacuoles in progenitor cells from bone marrow aspirates is a hallmark finding for this syndrome. Therefore, this study aimed to characterize leukocytes from VEXAS patients versus patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV), familial Mediterranean fever (FMF), and healthy donors (HD) to define a specific cytological pattern that can support VEXAS diagnosis. Twelve VEXAS patients were included in the study. Blood samples from FMF (n = 16), AAV (n = 16) and HDs (n = 20) acted as controls. May-Grünwald Giemsa (MGG) staining was used for studying cellular morphology, including cytoplasm, granules, and vacuoles and to perform a cytogenic evaluation of leucocytes. Plasma IL-1β, IL-1α, TNFα, IL-18 and IL-8 were measured using ELISA assay. The cytological analysis from blood smears confirmed the presence of immature neutrophils in VEXAS patients. We found a greater number of vacuoles in VEXAS patients vs. FMF, AAV and HD. Micronuclei (MNi) and cell death rate were higher in VEXAS patients vs. HD. Cell death correlated with IL-1β and IL-8 levels. MNi were positively associated with IL-8 and IL-1β levels, and with the percentage of immature neutrophils and vacuoles. In conclusion, our findings suggested that cytological test may be supportive for VEXAS diagnosis, despite genetical analysis is mandatory for confirming the disease. Finally, we identified several cytological hallmarks that may distinguish the VEXAS "cytotype" not only from HD but also from other inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: VEXAS; cytokines; cytology; hematology; inflammation; vacuoles.
Copyright © 2024 Baggio, Oliviero, Padoan, Iorio, Bixio, Orsolini, Bertoldo, Bernardi, Colavito, Paiero, Pregnolato, Ramonda, Doria, Bindoli and Sfriso.
Conflict of interest statement
AD received consultancy fees from GSK, Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Otsuka. PS received grants from Novartis and Sobi. Authors DC, BP and GP were employed by R&I Genetics srl. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

