The relationship between visual health and influencing factors among primary and secondary school students: a survey based in the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region of China
- PMID: 39421859
- PMCID: PMC11484000
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1457465
The relationship between visual health and influencing factors among primary and secondary school students: a survey based in the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region of China
Abstract
Introduction: The myopia rate of young people around the world, especially in China, has continued to rise, and the vision health of primary and secondary school students has gradually become a global concern. It was to explore the current characteristics of vision status and their intrinsic links to influencing factors of the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region primary and secondary school students under regional characteristics.
Methods: 1,670 primary and secondary school students in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region were surveyed using Vision examination, International Physical Activity Scale, Lifestyle Behavior Scale. The data were analyzed using SPSS 25.0 and AMOS 23.0.
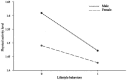
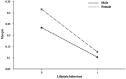
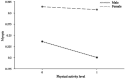
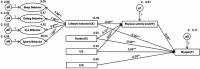
Results: The prevalence of myopia among primary and secondary school students in the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region was 27.3%, with rates of 31.5% for girls and 23.4% for boys. There was a significant negative correlation between lifestyle behaviors (r = -0.36, p < 0.01) and physical activity level (r = -0.06, p < 0.05) with vision status. The physical activity level played a significant masking effect between lifestyle behaviors and vision status (a*b = 0.002, c' = -0.044). Gender moderated the effects of lifestyle behaviors on physical activity level and vision status, as well as the effects of physical activity level on vision status. These factors constituted a mixed model with mediating and moderation. The model fitted well (RMSEA = 0.028, CFI = 0.951, NFI = 0.918).
Discussion: The prevalence of myopia among primary and secondary school students in this region is lower than the national average in China, and it is associated with lifestyle behaviors, physical activity level, and gender. When effectively controlled, the physical activity level significantly will reduce the prevalence of myopia as a masking variable. Gender, as a moderating variable, provides theoretical support for the classification and prevention of myopia. Regional surveys enriched the global database on adolescent myopia research, revealing the characteristics and common factors of visual problems in adolescents. Relevant departments and schools should integrate eye care into the national health security system, implement policies related to myopia prevention and control and safeguard the visual health of primary and secondary school students.
Keywords: gender; lifestyle behaviors; masking effect; moderating effect; myopia; physical activity level; visual health.
Copyright © 2024 Xu, Sang, Xu and Feng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The relationship between vision status and its influencing factors among primary and secondary school students: The masking effect of physical activity level and the moderating effect of academic stress.BMC Public Health. 2025 Feb 5;25(1):476. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21625-7. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39910514 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of visual impairment and refractive errors among different ethnic groups in schoolchildren in Turpan, China.Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2015 May;35(3):263-70. doi: 10.1111/opo.12193. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2015. PMID: 25783952
-
The Prevalence of Myopia and Its Association with Sleep Duration, Physical Activity, and Eye Exercises.Semin Ophthalmol. 2025 Apr 18:1-8. doi: 10.1080/08820538.2025.2492256. Online ahead of print. Semin Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40249389
-
[Prevalence of myopia and influencing factors among primary and middle school students in 6 provinces of China].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Jan;37(1):29-34. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2016.01.006. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 26822639 Chinese.
-
[Analysis of myopia detection rate and influencing factors among primary and secondary school students in Hunan Province in 2022].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2025 Jun 10;46(6):1014-1022. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20240912-00572. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40518396 Chinese.
Cited by
-
The relationship between vision status and its influencing factors among primary and secondary school students: The masking effect of physical activity level and the moderating effect of academic stress.BMC Public Health. 2025 Feb 5;25(1):476. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21625-7. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39910514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO (2019). WHO releases first world sight report. World Health Organization. Available at: https://www.who.int/zh/news/item/08-10-2019-who-launches-first-world-rep... (Accessed April 10, 2024).
-
- Hou S, Zhang XJ, Xu YQ, Yan SQ, Wang H, Gao GP, et al. . Study on the association between visual development and daily life conditions in preschool children. Chinese J Dis Control Prev. (2013) 17:222–5.
-
- Li T, Yang J, Yan J, Yao X, du B, Wu Q, et al. . Interaction between parental myopia and children lifestyle on the incidence of myopia among children aged 6-18 years: a cross-sectional study in Tianjin, China. BMJ Open. (2024) 14:e080929–9. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-080929, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

