Ferroptosis-Mediated Inflammation Promotes Pulmonary Hypertension
- PMID: 39421926
- PMCID: PMC11560515
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.324138
Ferroptosis-Mediated Inflammation Promotes Pulmonary Hypertension
Abstract
Background: Mitochondrial dysfunction, characterized by impaired lipid metabolism and heightened reactive oxygen species generation, results in lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. Ferroptosis is an inflammatory mode of cell death that promotes complement activation and macrophage recruitment. In pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), pulmonary arterial endothelial cells exhibit cellular phenotypes that promote ferroptosis. Moreover, there is ectopic complement deposition and inflammatory macrophage accumulation in the pulmonary vasculature. However, the effects of ferroptosis inhibition on these pathogenic mechanisms and the cellular landscape of the pulmonary vasculature are incompletely defined.
Methods: Multiomics and physiological analyses evaluated how ferroptosis inhibition-modulated preclinical PAH. The impact of adeno-associated virus 1-mediated expression of the proferroptotic protein ACSL (acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member) 4 on PAH was determined, and a genetic association study in humans further probed the relationship between ferroptosis and pulmonary hypertension.
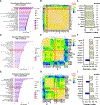
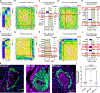
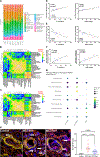
Results: Ferrostatin-1, a small-molecule ferroptosis inhibitor, mitigated PAH severity in monocrotaline rats. RNA-sequencing and proteomics analyses demonstrated ferroptosis was associated with PAH severity. RNA-sequencing, proteomics, and confocal microscopy revealed complement activation and proinflammatory cytokines/chemokines were suppressed by ferrostatin-1. In addition, ferrostatin-1 combatted changes in endothelial, smooth muscle, and interstitial macrophage abundance and gene activation patterns as revealed by deconvolution RNA-sequencing. Ferroptotic pulmonary arterial endothelial cell damage-associated molecular patterns restructured the transcriptomic signature and mitochondrial morphology, promoted the proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells, and created a proinflammatory phenotype in monocytes in vitro. Adeno-associated virus 1-Acsl4 induced an inflammatory PAH phenotype in rats. Finally, single-nucleotide polymorphisms in 6 ferroptosis genes identified a potential link between ferroptosis and pulmonary hypertension severity in the Vanderbilt BioVU repository.
Conclusions: Ferroptosis promotes PAH through metabolic and inflammatory mechanisms in the pulmonary vasculature.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; ferroptosis; hypertension, pulmonary; mitochondria.
Conflict of interest statement
K.W. Prins received grant funding from Bayer unrelated to this article. The other authors report no conflicts.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL162927/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 FD007627/FD/FDA HHS/United States
- K08 HL168166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL166843/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR007612/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R61 HL158941/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL146588/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD028717/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI165553/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F31 HL170585/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL155278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL158795/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL163960/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK124845/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

