Two weeks of exercise alters neuronal extracellular vesicle insulin signaling proteins and pro-BDNF in older adults with prediabetes
- PMID: 39421964
- PMCID: PMC11709104
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.14369
Two weeks of exercise alters neuronal extracellular vesicle insulin signaling proteins and pro-BDNF in older adults with prediabetes
Abstract
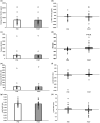
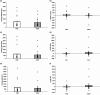
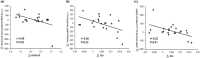
Adults with prediabetes are at risk for Alzheimer's Disease and Related Dementia (ADRD). While exercise may lower ADRD risk, the exact mechanism is unclear. We tested the hypothesis that short-term exercise would raise neuronal insulin signaling and pro-BDNF in neuronal extracellular vesicles (nEVs) in prediabetes. Twenty-one older adults (18F, 60.0 ± 8.6 yrs.; BMI: 33.5 ± 1.1 kg/m2) with prediabetes (ADA criteria; 75 g OGTT) were randomized to 12 supervised work-matched continuous (n = 13, 70% HRpeak) or interval (n = 8, 90% HRpeak and 50% HRpeak for 3 min each) sessions over 2-wks for 60 min/d. Aerobic fitness (VO2peak) and body weight were assessed. After an overnight fast, whole-body glucose tolerance (total area under the curve, tAUC) and insulin sensitivity (SIis) were determined from a 120 min 75 g OGTT. nEVs were acquired from 0 and 60 min time-points of the OGTT, and levels of insulin signaling proteins (i.e., p-IRS-1, total-/p-Akt, pERK1/2, pJNK1/2, and pp38) and pro-BNDF were measured. OGTT stimulatory effects were calculated from protein differences (i.e., OGTT 60-0 min). Adults were collapsed into a single group as exercise intensity did not affect nEV outcomes. Exercise raised VO2peak (+1.4 ± 2.0 mL/kg/min, p = 0.008) and insulin sensitivity (p = 0.01) as well as decreased weight (-0.4 ± 0.9 kg, p = 0.04) and whole-body glucose tAUC120min (p = 0.02). Training lowered 0-min pro-BDNF (704.1 ± 1019.0 vs. 414.5 ± 533.5, p = 0.04) and increased OGTT-stimulated tAkt (-51.8 ± 147.2 vs. 95 ± 204.5 a.u., p = 0.01), which was paralleled by reduced pAkt/tAkt at 60 min of the OGTT (1.3 ± 0.2 vs. 1.2 ± 0.1 a.u., p = 0.04). Thus, 2 weeks of exercise altered neuronal insulin signaling responses to glucose ingestion and lowered pro-BNDF among adults with prediabetes, thereby potentially lowering ADRD risk.
Keywords: aging; glucose tolerance; insulin sensitivity; obesity; physical activity; type 2 diabetes.
© 2024 The Author(s). Aging Cell published by Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
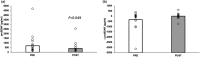
References
-
- Arnold, S. E. , Arvanitakis, Z. , Macauley‐Rambach, S. L. , Koenig, A. M. , Wang, H.‐Y. , Ahima, R. S. , & Nathan, D. M. (2018). Brain insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer disease: Concepts and conundrums. Nature Reviews. Neurology, 14(3), 168–181. 10.1038/nrneurol.2017.185 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Babaei, P. , Azali Alamdari, K. , Soltani Tehrani, B. , & Damirchi, A. (2013). Effect of six weeks of endurance exercise and following detraining on serum brain derived neurotrophic factor and memory performance in middle aged males with metabolic syndrome. The Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness, 53(4), 437–443. - PubMed
-
- Bastard, J. P. , Vandernotte, J. M. , Faraj, M. , Karelis, A. D. , Messier, L. , Malita, F. M. , Garrel, D. , Prud'homme, D. , & Rabasa‐Lhoret, R. (2007). Relationship between the hyperinsulinemic‐euglycaemic clamp and a new simple index assessing insulin sensitivity in overweight and obese postmenopausal women. Diabetes & Metabolism, 33(4), 261–268. 10.1016/j.diabet.2007.02.004 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Blommer, J. , Pitcher, T. , Mustapic, M. , Eren, E. , Yao, P. J. , Vreones, M. P. , Pucha, K. A. , Dalrymple‐Alford, J. , Shoorangiz, R. , Meissner, W. G. , Anderson, T. , & Kapogiannis, D. (2023). Extracellular vesicle biomarkers for cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease. Brain: A Journal of Neurology, 146(1), 195–208. 10.1093/brain/awac258 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Broadhouse, K. M. , Singh, M. F. , Suo, C. , Gates, N. , Wen, W. , Brodaty, H. , Jain, N. , Wilson, G. C. , Meiklejohn, J. , Singh, N. , Baune, B. T. , Baker, M. , Foroughi, N. , Wang, Y. , Kochan, N. , Ashton, K. , Brown, M. , Li, Z. , Mavros, Y. , … Valenzuela, M. J. (2020). Hippocampal plasticity underpins long‐term cognitive gains from resistance exercise in MCI. NeuroImage Clinical, 25, 102182. 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102182 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

