How Are We Addressing Axial Psoriatic Arthritis in Clinical Practice?
- PMID: 39422869
- PMCID: PMC11557781
- DOI: 10.1007/s40744-024-00722-w
How Are We Addressing Axial Psoriatic Arthritis in Clinical Practice?
Abstract
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting the musculoskeletal system, skin and nails. In addition to peripheral joints, inflammation of the spine and sacroiliac joints may occur. Yet, research into this axial phenotype has lagged behind partly because of the challenge in its clinical identification with a lack of specific clinical, molecular or imaging biomarkers. In the absence of a validated definition of what constitutes axial PsA (axPsA), guidelines for the management of axial involvement in PsA in clinical practice are scarce. On the basis of a literature review and their clinical expertise, a group of rheumatology experts provide their opinion to aid the diagnosis and management of axial PsA in clinical practice.
Keywords: Axial involvement; Axial psoriatic arthritis; Axial spondyloarthritis; Psoriatic arthritis; Psoriatic spondylitis; Sacroiliitis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


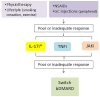
References
-
- Ritchlin CT, Colbert RA, Gladman DD. Psoriatic arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:957–70. - PubMed
-
- Michelena X, Poddubnyy D, Marzo-Ortega H. Axial psoriatic arthritis: a distinct clinical entity in search of a definition. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2020;46:327–41. - PubMed
-
- Feld J, Chandran V, Haroon N, Inman R, Gladman D. Axial disease in psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis: a critical comparison. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018;14:363–71. - PubMed
-
- Battistone MJ, Manaster BJ, Reda DJ, Clegg DO. The prevalence of sacroilitis in psoriatic arthritis: new perspectives from a large, multicenter cohort. A Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study. Skeletal Radiol. 1999;28:196–201. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

