Heterogeneity in oligodendrocyte precursor cell proliferation is dynamic and driven by passive bioelectrical properties
- PMID: 39423130
- PMCID: PMC11602547
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114873
Heterogeneity in oligodendrocyte precursor cell proliferation is dynamic and driven by passive bioelectrical properties
Abstract
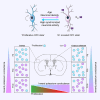
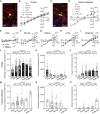
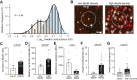
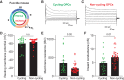
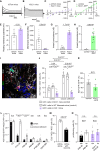
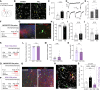
Oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs) generate myelinating oligodendrocytes and are the main proliferative cells in the adult central nervous system. OPCs are a heterogeneous population, with proliferation and differentiation capacity varying with brain region and age. We demonstrate that during early postnatal maturation, cortical, but not callosal, OPCs begin to show altered passive bioelectrical properties, particularly increased inward potassium (K+) conductance, which correlates with G1 cell cycle stage and affects their proliferation potential. Neuronal activity-evoked transient K+ currents in OPCs with high inward K+ conductance potentially release OPCs from cell cycle arrest. Eventually, OPCs in all regions acquire high inward K+ conductance, the magnitude of which may underlie differences in OPC proliferation between regions, with cells being pushed into a dormant state as they acquire high inward K+ conductance and released from dormancy by synchronous neuronal activity. Age-related accumulation of OPCs with high inward K+ conductance might contribute to differentiation failure.
Keywords: CP: Neuroscience; Kir channels; aging; bioelectricity; cell cycle; cell states; glia; oligodendrocyte precursor cell; potassium; proliferation; stem cell.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Gautier H.O.B., Evans K.A., Volbracht K., James R., Sitnikov S., Lundgaard I., James F., Lao-Peregrin C., Reynolds R., Franklin R.J.M., Káradóttir R.T. Neuronal activity regulates remyelination via glutamate signalling to oligodendrocyte progenitors. Nat. Commun. 2015;6:8518. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9518. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

