Astrocytic GLUT1 reduction paradoxically improves central and peripheral glucose homeostasis
- PMID: 39423276
- PMCID: PMC11488540
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adp1115
Astrocytic GLUT1 reduction paradoxically improves central and peripheral glucose homeostasis
Abstract
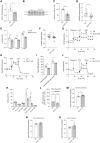
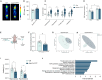
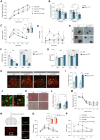
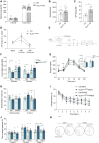
Astrocytes are considered an essential source of blood-borne glucose or its metabolites to neurons. Nonetheless, the necessity of the main astrocyte glucose transporter, i.e., GLUT1, for brain glucose metabolism has not been defined. Unexpectedly, we found that brain glucose metabolism was paradoxically augmented in mice with astrocytic GLUT1 reduction (GLUT1ΔGFAP mice). These mice also exhibited improved peripheral glucose metabolism especially in obesity, rendering them metabolically healthier. Mechanistically, we observed that GLUT1-deficient astrocytes exhibited increased insulin receptor-dependent ATP release, and that both astrocyte insulin signaling and brain purinergic signaling are essential for improved brain function and systemic glucose metabolism. Collectively, we demonstrate that astrocytic GLUT1 is central to the regulation of brain energetics, yet its depletion triggers a reprogramming of brain metabolism sufficient to sustain energy requirements, peripheral glucose homeostasis, and cognitive function.
Figures



References
-
- Bélanger M., Allaman I., Magistretti P. J., Brain energy metabolism: Focus on astrocyte-neuron metabolic cooperation. Cell Metab. 14, 724–738 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Mink J. W., Blumenschine R. J., Adams D. B., Ratio of central nervous system to body metabolism in vertebrates: its constancy and functional basis. Am. J. Physiol. 241, R203–R212 (1981). - PubMed
-
- M. C. McKenna, R. Gruetter, U. Sonnewald, H. S. Waagepetersen, A. Schousboe, “Energy metabolism of the brain” in Basic Neurochemistry: Molecular, Cellular and Medical Aspects, G. J. Siegel, R. W. Alberts, S. T. Brady, D. L. Price, Eds. (Elsevier Academic Press, Burlington, MA, ed. 7, 2006), pp. 531–557.
-
- E. L. Roberts, “The support of energy metabolism in the central nervous system with substrates other than glucose” in Handbook of Neurochemistry and Molecular Neurobiology: Brain Energetics. Integration of Molecular and Cellular Processes, A. Lajtha, G. E. Gibson, G. A. Dienel, Eds. (Springer, 2007), pp. 137–179; 10.1007/978-0-387-30411-3_7. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

