MicroRNA-130a-3p regulates osimertinib resistance by targeting runt-related transcription factor 3 in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 39424918
- PMCID: PMC11489462
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-76196-1
MicroRNA-130a-3p regulates osimertinib resistance by targeting runt-related transcription factor 3 in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
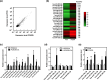
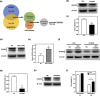
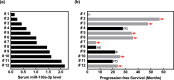
Overcoming resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors, including osimertinib, is urgent to improve lung cancer treatment outcomes. Extracellular vesicle (EV)-derived microRNAs (EV-miRNAs) play important roles in drug resistance and serve as promising biomarkers. In this study, we aimed to identify EV-miRNAs associated with osimertinib resistance and investigate their clinical relevance. The release of excess EVs was confirmed in the osimertinib-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cell line PC9OR. The exposure of PC9OR-derived EVs and EV-miRNAs to PC9 cells increased cell viability after osimertinib treatment. Microarray analysis revealed that miR-130a-3p was upregulated in EVs derived from PC9OR cells and another osimertinib-resistant cell line (H1975OR). Transfection with miR-130a-3p attenuated osimertinib-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in both PC9 and H1975 cells, whereas osimertinib resistance in PC9OR cells was reversed after miR-130a-3p inhibition. Bioinformatics analysis revealed that runt-related transcription factor 3 is a target gene of miR-130a-3p, and it induced osimertinib resistance in PC9 cells. Patients with lower baseline serum miR-130a-3p concentrations had longer progression-free survival. miR-130a-3p is a potential therapeutic target and a predictive biomarker of osimertinib resistance in adenocarcinomas.
Keywords: Extracellular vesicles; Lung adenocarcinoma; MicroRNA-130a-3p; Osimertinib resistance; Runt-related transcription factor 3.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Torre, L. A. et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin.65, 87–108 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Sung, H. et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin.71, 209–249 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Hirsch, F. R. et al. Lung cancer: current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet. 389, 299–311 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Thai, A. A., Solomon, B. J., Sequist, L. V., Gainor, J. F. & Heist, R. S. Lung cancer. Lancet. 398, 535–554 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

