The association between maternal anemia and neonatal anemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39425056
- PMCID: PMC11488222
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-024-06832-1
The association between maternal anemia and neonatal anemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Importance: Neonatal anemia has a long-term effect on children's growth and development. Anemia during pregnancy is also the most widespread nutritional deficiency among pregnant women in the world; If it leads to anemia in newborns, it will affect a wide range of people and be a public health problem worthy of attention.
Objective: To study the relationship between maternal anemia during pregnancy and neonatal hemoglobin levels.
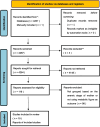
Data sources: PubMed, Web of science, Scopus, MEDLINE, Embase, ProQuest, Dissertations & Theses Global, The Cochrane Library, China Biology Medicine Database, Chinese CNKI Database, and Chinese Wanfang Database were systematically searched from inception to August 31, 2022.
Study selection: The meta-analysis included all original studies which pertain to cohort studies, case-control studies or cross-sectional studies that investigated the relationship between maternal anemia during pregnancy and neonatal hemoglobin levels.
Data extraction and synthesis: Hemoglobin level of both anemic and non-anemic pregnant mothers and their paired newborns were pooled from the selected studies. The random-effects model was used to assess the risk of getting a lower neonatal hemoglobin level between mothers with and without pregnant anemia. Data analyses were performed from September 5, 2022, to March 10, 2023.
Main outcomes and measures: Maternal anemia during pregnancy is a risk factor of lower neonatal hemoglobin levels.
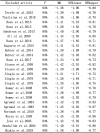
Results: The initial search yielded 4267 records of which 116 articles underwent full-text evaluation, which identified 18 articles and a total of 1873 patients that were included. The findings of the meta-analysis showed a significant difference between the two groups(MD=-1.38; 95%CI:[-1.96,-0.80]. p<0.01), while the co-effect showed that the neonatal hemoglobin value of anemic mothers was 1.38g/dL lower than that of non-anemic mothers(-1.96,-0.80), suggesting a correlation between maternal anemia lower neonatal hemoglobin levels.
Conclusions and relevance: This systematic review and meta-analysis demonstrated that maternal anemia during pregnancy were associated with a lower level of newborn hemoglobin levels. This may enable a better understanding of neonatal anemia and provide guidance towards future development of nutritional supplementation during pregnancy and the prediction of postpartum outcomes.
Trial registration: PROSPERO Identifier: CRD42022352759.
Keywords: Infants; Iron deficiency; Maternal anemia; Nutrition.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- World health statistics 2022: monitoring health for the SDGs, sustainable development goals. Accessed 31 Aug 2024. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240051157.
-
- Global anaemia reduction efforts among women of reproductive age: impact, achievement of targets and the way forward for optimizing efforts. Accessed 31 Aug 2024. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240012202.
-
- Global nutrition monitoring framework: operational guidance for tracking progress in meeting targets for 2025. Accessed 31 Aug 2024. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241513609.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

