R-loops' m6A modification and its roles in cancers
- PMID: 39425197
- PMCID: PMC11487993
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-024-02148-y
R-loops' m6A modification and its roles in cancers
Abstract
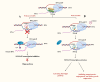
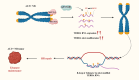
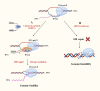
R-loops are three-stranded nucleic acid structures composed of an RNA-DNA hybrid and a displaced DNA strand. They are widespread and play crucial roles in regulating gene expression, DNA replication, and DNA and histone modifications. However, their regulatory mechanisms remain unclear. As R-loop detection technology advances, changes in R-loop levels have been observed in cancer models, often associated with transcription-replication conflicts and genomic instability. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is an RNA epigenetic modification that regulates gene expression by affecting RNA localization, splicing, translation, and degradation. Upon reviewing the literature, we found that R-loops with m6A modifications are implicated in tumor development and progression. This article summarizes the molecular mechanisms and detection methods of R-loops and m6A modifications in gene regulation, and reviews recent research on m6A-modified R-loops in oncology. Our goal is to provide new insights into the origins of genomic instability in cancer and potential strategies for targeted therapy.
Keywords: Cancer; Gene expression; M6A modification; R-loop.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

