Secukinumab efficacy in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa assessed by the International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Score System (IHS4): A post hoc analysis of the SUNSHINE and SUNRISE trials
- PMID: 39425517
- PMCID: PMC12291009
- DOI: 10.1111/jdv.20369
Secukinumab efficacy in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa assessed by the International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Score System (IHS4): A post hoc analysis of the SUNSHINE and SUNRISE trials
Abstract
Introduction: The International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Score System (IHS4) is a validated tool that measures inflammatory lesions, including draining tunnels, in hidradenitis suppurativa (HS).
Objective: To evaluate secukinumab efficacy using IHS4 in patients with moderate to severe HS.
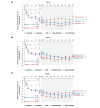
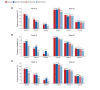
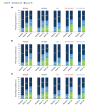
Methods: Data from the SUNSHINE and SUNRISE trials, which assessed subcutaneous secukinumab 300 mg every 2 (SECQ2W) and 4 (SECQ4W) weeks in adults with moderate to severe HS, were analyzed. Assessments included changes from baseline in IHS4 and severity classification up to Week 52; IHS4-55, IHS4-75, IHS4-90 responses (55%, 75% and 90% reduction in IHS4) and concordance between IHS4-55 and HS clinical response (HiSCR), at Weeks 16 and 52.
Results: In total, 1084 patients (SECQ2W = 361; SECQ4W = 360; placebo = 363) were analyzed. At Week 16, SECQ2W and SECQ4W demonstrated a numerically higher reduction in IHS4 from baseline versus placebo (adjusted mean [95% CI]: -10.80 [-12.30 to -9.30] and -9.46 [-10.96 to -7.96] vs. -4.92 [-6.43 to -3.41]); the reduction was maintained until Week 52 in both dose regimens. A greater proportion of patients achieved IHS4-55 with SECQ2W (43.4%) and SECQ4W (39.5%) versus placebo (31.5%) at Week 16, with further improvement at Week 52. Similar trends were observed for IHS4-75 and IHS4-90 responses. While no patients had mild disease based on IHS4 (80.7% had severe and 19.3% had moderate HS) at baseline, a greater proportion of patients were categorized as having mild disease at Week 16 in the SECQ2W (25.9%) and SECQ4W (24.0%) groups versus placebo (16.4%); this trend continued up to Week 52 in both dose regimens. Strong concordance (>85%) was observed between IHS4-55 and HiSCR.
Conclusions: Both SECQ2W and SECQ4W demonstrated efficacy in improving treatment response as measured by IHS4 and reducing disease severity versus placebo at Week 16 and these improvements were sustained through Week 52. These findings support that the dynamic and dichotomous IHS4 can efficiently detect treatment response changes in clinical trial settings.
Clinical trials registration: SUNSHINE (NCT03713619); SUNRISE (NCT03713632).
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Conflict of interest statement
Christos C. Zouboulis reports consultancy/advisory board/lecture fee disease‐relevant honoraria from Almirall, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Idorsia, Incyte, InflaRx, Novartis, Sanofi and UCB. He is the president of the EHSF e.V., coordinator of the ALLOCATE Skin group of the ERN Skin and chair of the ARHS Task Force group of the EADV. He is the editor of the EADV News and the copyright co‐holder of IHS4 on behalf of the EHSF e.V. His employer has received disease‐relevant clinical study fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, InflaRx, Novartis and UCB for his participation as clinical investigator. Athanassios Kyrgidis declares no conflict of interest. Afsaneh Alavi reports consultancy fees from AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Incyte, InflaRx Novartis and UCB; she is a principal investigator for Boehringer Ingelheim and Process and serves on the board of EHSF. Gregor B. E. Jemec reports consultancy fees from Novartis and UCB, has received grants from Abbvie, Chemocentryx, LEO, InflaRx, Novartis and UCB and support for attending meetings from Sanofi. He is the vice president of the EHSF e.V. and in the board of C3 and CHORD and is co‐coordinator of the ALLOCATE Skin group of the ERN Skin and vice chair of the ARHS Task Force group of the EADV. He is editor‐in‐chief of dermatology. Antonio Martorell has acted as a consultant, advisory board member and investigator and received honoraria from Novartis, AbbVie, Janssen Cilag, UCB, Lilly, LEO Pharma, L'Oreal, Sanofi, Sandoz, Boehringer Ingelheim and Amgen. Angelo V. Marzano reports consultancy/advisory boards' disease‐relevant honoraria from AbbVie, Boehringer‐Ingelheim, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi and UCB. Hessel H. van der Zee reports personal fees from AbbVie, InflaRx, Novartis, Galderma and Incyte. Magdalena B. Wozniak, Angela Llobet Martinez, Torben Kasparek, Teresa Bachhuber, Christine‐Elke Ortmann, Nicolas Thomas and Shoba Ravichandran are employees of Novartis. Iryna Lobach was an employee of Novartis at the time of the study. Thrasyvoulos Tzellos reports consultancy/advisory boards/speaker fees from AbbVie, Novartis, Boehringer‐Ingelheim and UCB. He is the treasurer of the EHSF e.V.
Figures

References
-
- Zouboulis CC, Del Marmol V, Mrowietz U, Prens EP, Tzellos T, Jemec GB. Hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa: criteria for diagnosis, severity assessment, classification and disease evaluation. Dermatology. 2015;231:184–190. - PubMed
-
- Zouboulis CC, Gulliver W, Ingram J, Kirby B, Giamarellos‐Bourboulis EJ, Podda M, et al. Endpoints of clinical trials for hidradenitis suppurativa: proceedings of a round‐table session. Exp Dermatol. 2020;29(Suppl 1):67–72. - PubMed
-
- Kimball AB, Sobell JM, Zouboulis CC, Gu Y, Williams DA, Sundaram M, et al. HiSCR (hidradenitis suppurativa clinical response): a novel clinical endpoint to evaluate therapeutic outcomes in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa from the placebo‐controlled portion of a phase 2 adalimumab study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:989–994. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hurley HJ. Axillary hyperhidrosis, apocrine bromhidrosis, hidradenitis suppurativa and familial benign pemphigus: surgical approach. In: Roenigk RK, Roenigk HH Jr, editors. Dermatologic Surgery. Principles and Practice. 2nd ed. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker; 1996. p. 623–645.

