Case of Successful Sympathetic Nerve Modulation by Targeted Heavy Ion Radiotherapy for Idiopathic Ventricular Tachycardia
- PMID: 39425937
- PMCID: PMC11490255
- DOI: 10.1111/anec.70020
Case of Successful Sympathetic Nerve Modulation by Targeted Heavy Ion Radiotherapy for Idiopathic Ventricular Tachycardia
Abstract
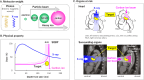
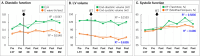
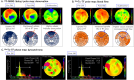
Non-invasive radioablation using stereotactic body radiation therapy with X-ray has been proposed as a rescue treatment for refractory ventricular tachycardia (VT). However, there are concerns about the occurrence of late valvular or coronary disease. We treated VT originating from the aortic sinus cusp using the Bragg peak principle of a heavy ion beam, minimizing the dose to the aortic valve and coronary artery and providing an anti-arrhythmic effect and cardiac function recovery due to improved sympathetic nerve heterogeneity. We present a method for targeting sympathetic nerve distribution using 123I-metaiodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy.
Keywords: 123I‐metaiodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy; arrhythmia radioablation; non‐invasive irradiation technique; sympathetic denervation; targeted heavy ion radiotherapy; ventricular arrhythmia.
© 2024 The Author(s). Annals of Noninvasive Electrocardiology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Balgobind, B. V. , Visser J., Grehn M., et al. 2023. “Refining Critical Structure Contouring in STereotactic Arrhythmia Radioablation (STAR): Benchmark Results and Consensus Guidelines From the STOPSTORM.Eu Consortium.” Radiotherapy and Oncology 189: 109949. 10.1016/j.radonc.2023.109949. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

