Sprayable inflammasome-inhibiting lipid nanorods in a polymeric scaffold for psoriasis therapy
- PMID: 39426974
- PMCID: PMC11490495
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-53396-x
Sprayable inflammasome-inhibiting lipid nanorods in a polymeric scaffold for psoriasis therapy
Abstract
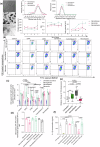
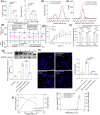
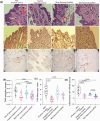
Localized delivery of inflammasome inhibitors in phagocytic macrophages could be promising for psoriasis treatment. The present work demonstrates the development of non-spherical lipid nanoparticles, mimicking pathogen-like shapes, consisting of an anti-inflammatory inflammasome inhibiting lipid (pyridoxine dipalmitate) as a trojan horse. The nanorods inhibit inflammasome by 3.8- and 4.5-fold compared with nanoellipses and nanospheres, respectively. Nanorods reduce apoptosis-associated speck-like protein and lysosomal rupture, restrain calcium influx, and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Dual inflammasome inhibitor (NLRP3/AIM-2-IN-3) loaded nanorods cause synergistic inhibition by 21.5- and 59-folds compared with nanorods and free drug, respectively alongside caspase-1 inhibition. The NLRP3/AIM-2-IN-3 nanorod when transformed into a polymeric scaffold, simultaneously and effectively inhibits RNA levels of NLRP3, AIM2, caspase-1, chemokine ligand-2, gasdermin-D, interleukin-1β, toll-like receptor 7/ 8, and IL-17A by 6.4-, 1.6-, 2.0-, 13.0-, 4.2-, 24.4-, 4.3-, and 1.82-fold, respectively in psoriatic skin in comparison to Imiquimod positive control group in an in-vivo psoriasis-like mice model.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
D.S. and A.K. has filed a patent application on this research. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Armstrong, A. W. & Read, C. Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment of Psoriasis: A Review. JAMA - J. Am. Med. Assoc.323, 1945–1960 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Global Report on Psoriasis; 2016.
-
- Yamanaka, K., Yamamoto, O. & Honda, T. Pathophysiology of Psoriasis: A Review. J. Dermatol.48, 722–731 (2021). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

