Biologically informed deep neural networks provide quantitative assessment of intratumoral heterogeneity in post treatment glioblastoma
- PMID: 39427044
- PMCID: PMC11490546
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-024-01277-4
Biologically informed deep neural networks provide quantitative assessment of intratumoral heterogeneity in post treatment glioblastoma
Abstract
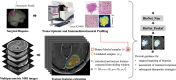
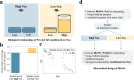
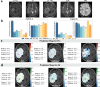
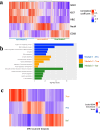
Intratumoral heterogeneity poses a significant challenge to the diagnosis and treatment of recurrent glioblastoma. This study addresses the need for non-invasive approaches to map heterogeneous landscape of histopathological alterations throughout the entire lesion for each patient. We developed BioNet, a biologically-informed neural network, to predict regional distributions of two primary tissue-specific gene modules: proliferating tumor (Pro) and reactive/inflammatory cells (Inf). BioNet significantly outperforms existing methods (p < 2e-26). In cross-validation, BioNet achieved AUCs of 0.80 (Pro) and 0.81 (Inf), with accuracies of 80% and 75%, respectively. In blind tests, BioNet achieved AUCs of 0.80 (Pro) and 0.76 (Inf), with accuracies of 81% and 74%. Competing methods had AUCs lower or around 0.6 and accuracies lower or around 70%. BioNet's voxel-level prediction maps reveal intratumoral heterogeneity, potentially improving biopsy targeting and treatment evaluation. This non-invasive approach facilitates regular monitoring and timely therapeutic adjustments, highlighting the role of ML in precision medicine.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Update of
-
Biologically-informed deep neural networks provide quantitative assessment of intratumoral heterogeneity in post-treatment glioblastoma.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 27:rs.3.rs-3891425. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3891425/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: NPJ Digit Med. 2024 Oct 19;7(1):292. doi: 10.1038/s41746-024-01277-4. PMID: 38585856 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

