Attrition between lines of therapy and real-world outcomes of patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer in Europe: a cohort study leveraging electronic medical records
- PMID: 39427280
- PMCID: PMC11785661
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-024-07506-4
Attrition between lines of therapy and real-world outcomes of patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer in Europe: a cohort study leveraging electronic medical records
Abstract
Purpose: To characterize real-world attrition rates across first-line (1L) to third-line (3L) therapies in patients with HER2-positive (HER2 +) metastatic breast cancer (mBC) receiving routine care in seven hospital systems across Europe (France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and the UK).
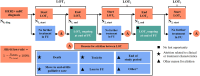
Methods: This retrospective, observational, multi-country, cohort study collected electronic medical record data from women aged ≥ 18 years diagnosed with HER2 + mBC from 2017-2021. The primary endpoint was attrition rate (the proportion of patients receiving a line of therapy [LOT] with no further evidence of subsequent LOTs). Key additional endpoints included treatment patterns, real-world time to treatment discontinuation (TTD), and time to next treatment (TTNT).
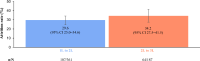
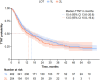
Results: 29.6% (95% confidence interval [CI] 25.0-34.6) and 34.2% (95% CI 27.5-41.5) of treated patients with HER2 + mBC had no further evidence of treatment beyond 1L and second-line (2L) therapy, respectively. Attrition was primarily owing to death, move to end-of-life palliative care, loss to follow up, and "other" reasons. Treatment patterns were generally aligned with clinical guidelines. Decreases in TTD (12.1 months [95% CI 10.4-14.5] for 1L, 8.9 months [95% CI 7.3-11.9] for 2L, 6.4 months [95% CI 5.2-8.9] for 3L) and TTNT (15.4 months [95% CI 13.6-20.6] for 1L, 13.5 months [95% CI 10.8-19.4] for 2L) were observed with each subsequent LOT.
Conclusion: Results unveil a large proportion of patients who do not benefit from state-of-the-art subsequent LOT, and suggest diminishing effectiveness with each subsequent LOT.
Keywords: Attrition; Breast neoplasm; ERBB2 protein; HER2; Neoplasm metastasis; Real-world data.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare the following competing interests: N.H. has received lecture honoraria from Art Tempi, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Gilead, Lilly, Medscape, MSD, Novartis, Onkowissen, Pierre Fabre, Roche, Sanofi, Seagen, Viatris, and Zuelligpharma; has received consulting or advisory honoraria from Aptitude Health, Gilead, Pfizer, Sandox-Hexal, Sanofi, and Seagen; has received research funding from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Gilead, MSD, Roche, Seagen, TRIO, and WSG; has participated on IDMC/steering committees for Lilly, Pierre Fabre, and Roche; and has ownership interest in the West German Study Group. E.C. has received lecture, consulting, or advisory honoraria from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Gilead, Lilly, Menarini, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Reveal Genomics, and Roche; has received support for attending meetings and/or travel from AstraZeneca, Pfizer, and Roche; has received research funding from Daiichi Sankyo, Pfizer, and Roche; and has participated on steering committees for AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Gilead, Novartis, Reveal Genomics, and Roche. G.J. has received consulting honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Diaccurate, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and Seagen; has received honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and Seagen; has received support for attending meetings and/or travel from Amgen, AstraZeneca Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche; and has received medical writing support from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Lilly, Novartis, and Roche. V.M. has received lecture honoraria from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Gilead, high5 Oncology, iMED Institut, Lilly, Medac, Medscape, MSD, Novartis, Onkowissen, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Roche, and Seagen; has received consulting or advisory honoraria from ClinSol, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Gilead, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, PINK, Roche, and Stemline; and has received research funding from AstraZeneca, Genentech, Novartis, Roche, and Seagen. N.N. has received consulting or advisory honoraria from AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharmaceutical, and Daiichi Sankyo; has received lecture honoraria from AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Eisai, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly Japan, Nippon Kayaku, and Pfizer Japan; and has received research funding from Chugai Pharmaceutical, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly Japan, Nippon Kayaku, and Pfizer Japan. G.V. has received research grants from Dako/Agilent Technologies, Roche/Genentech, and Ventana Medical Systems, and has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Dako/Agilent, Gilead, MSD Oncology, Pfizer, Roche, and Ventana. R.B. has held advisory roles at AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Grünenthal, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Roche, Seagen, and Stemline; has received lecture honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Grünenthal, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Roche, Seagen, and Stemline; and has received research support from Daiichi Sankyo, MSD, Novartis, and Roche. C.K. has received lecture honoraria from AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Genomic Health, Gilead, GSK, Novartis, PharmaMar, Pfizer, and Roche; has received consulting or advisory honoraria from AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Genomic Health, Gilead, GSK, MSD, Novartis, PharmaMar, and Roche; and has participated on steering committees for AstraZeneca. M.J.H. has received lecture honoraria from AstraZeneca. R.M.C. has received an unrestricted educational grant from Pfizer; has received research support from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, MSD Ireland, and Pfizer; has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Gilead, Lilly, and Seagen; and has received support for attending meetings and/or travel from Gilead, Novartis, and Roche. M.G. has received support for attending meetings and/or travel from AstraZeneca, Gilead, Roche, and Pfizer, and has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Gilead, and Pfizer. V.G. has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Exact Sciences, Gilead, Menarini Stemline, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Olema Oncology, Pierre Fabre, and Roche; has received lecture honoraria from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Exact Sciences, Gilead, GSK, Menarini Stemline, Novartis, Roche, and Zentiva; and has received expert testimony honoraria from Eli Lilly. G.B. has received honoraria from Agendia, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Exact Science, Gilead, Helsinn Lilly, Menarini Stemline, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, and Seagen, and has received a research grant from Gilead. H.W. has received lecture honoraria from Seagen; has received consulting or advisory honoraria from AstraZeneca, Augustine Therapeutics, Daiichi Sankyo, E Squared Communications LLC, Gilead, Immutep Ltd, Lilly, MediMix, Novartis, NV Hict, Pfizer, PSI CRO, Roche, and Stemline Therapeutics; has received support for attending meetings and/or travel from Daiichi Sankyo and Pfizer; has received research funding from Novartis, Roche, and Syneos Health; and has received subscription fees from Gilead. S.E.-d-R. has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, COR2ED, Daiichi Sankyo, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Medistream, Pierre Fabre, Roche, and Seagen; has received research funding from AstraZeneca, Byondis, Daiichi Sankyo, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, MEDSIR, Roche, SOLTI, and Zymeworks; and has received support for attending meetings and/or travel from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Kern Pharma, Pfizer, Seagen, and SOLTI. M.P., H.B., N.K.-C., N.S., and S.V. are employees of AstraZeneca. N.K.-C. holds stocks in AstraZeneca and AbbVie. N.U.L. has received honoraria from AstraZeneca and has received research funding from AstraZeneca. The remaining authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: The study protocol was approved by Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli IRCCS Comitato Etico, Medizinische Ethikkommission an der Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg (for University Hospital Wurzburg and Vivantes Hospital Group), HRA and Health and Care Research Wales (for Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust and NHS Lothian, UK), CEIM Provincial de Málaga (for Unidad de Gestión Clínica Intercentros Oncology, Spain), and Comite de Revue Interne Data (for Institut Curie, France; study MR-004 compliant). Consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent to publish: Not applicable.
Figures

References
-
- European Cancer Information System (ECIS) (2022) Breast cancer in the EU. https://ecis.jrc.ec.europa.eu/. Accessed 28 Nov 2023
-
- Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Hicks DG et al (2013) Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol 31:3997–4013. 10.1200/JCO.2013.50.9984 - PubMed
-
- Howlader N, Cronin KA, Kurian AW, Andridge R (2018) Differences in breast cancer survival by molecular subtypes in the United States. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 27:619–626. 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-17-0627 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

