Does Injectable Platelet-Rich Fibrin Combined With Autogenous Demineralized Dentine Enhance Alveolar Ridge Preservation? A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 39429193
- PMCID: PMC11810550
- DOI: 10.1111/clr.14372
Does Injectable Platelet-Rich Fibrin Combined With Autogenous Demineralized Dentine Enhance Alveolar Ridge Preservation? A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Objective: The present trial evaluated the first-time application of autogenous demineralized dentin graft with injectable platelet-rich fibrin (ADDG + i-PRF) versus autogenous demineralized dentin graft (ADDG), in alveolar ridge preservation (ARP) in the maxillary aesthetic zone.
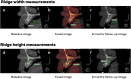
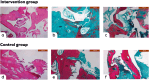
Material and methods: Twenty-two maxillary (n = 22) non-molar teeth indicated for extraction were randomized into two groups (n = 11/group). Extracted teeth were prepared into ADDG, implanted into extraction sockets with or without i-PRF amalgamation and covered by collagen sponge. Cone-beam computed tomography scans at baseline and 6 months were compared to assess ridge-dimensional changes. Keratinized tissue width, patient satisfaction, pain score and chair time were recorded. In the course of dental implant placements at 6 months, bone core biopsies of engrafted sites were obtained and analysed histomorphometrically.
Results: Reduction in ridge width was 1.71 ± 1.08 and 1.8 ± 1.35 mm, while reduction in ridge height was 1.11 ± 0.76 and 1.8 ± 0.96 mm for ADDG + i-PRF and ADDG, respectively (p > 0.05). Significant differences in keratinized tissue width reduction were notable between ADDG + i-PRF and ADDG (0.12 ± 0.34 and 0.58 ± 0.34 mm respectively; p = 0.008). Postoperative pain scores were significantly lower in ADDG + i-PRF (p = 0.012). All patients in the two groups were satisfied with no differences in chair time (p > 0.05). No differences in total percentage area of newly formed bone, soft tissue or graft particles were observed between the groups (p > 0.05).
Conclusions: ADDG alone or in combination with i-PRF yields similar results regarding ARP clinically, quality of the formed osseous tissues, as well as patients' satisfaction. Yet, the addition of i-PRF to ADDG tends to preserve the keratinized tissue and lessen postoperative pain.
Keywords: alveolar; autogenous; dentin; extraction; platelets; preservation.
© 2024 The Author(s). Clinical Oral Implants Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abdulrahman, Y. A. , Hosny M. M., Elfana A., and Fawzy El‐Sayed K. M.. 2022. “Clinical and Radiographic Evaluation of Low‐Speed Platelet‐Rich Fibrin (PRF) for the Treatment of Intra‐Osseous Defects of Stage‐III Periodontitis Patients: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial.” Clinical Oral Investigations 26, no. 11: 6671–6680. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al Qabbani, A. , Razak N. H. A., Al Kawas S., Hamid S. S. A., Wahbi S., and Samsudin A.. 2017. “The Efficacy of Immediate Implant Placement in Extraction Sockets for Alveolar Bone Preservation: A Clinical Evaluation Using Three‐Dimensional Cone Beam Computerized Tomography and Resonance Frequency Analysis Value.” Journal of Craniofacial Surgery 28, no. 4: e318–e325. - PubMed
-
- Alazzawi, A. , Ghazi M., and Jikia M.. 2018. “Complications During and After Extraction of Third Molar.” Caucasus Journal of Health Sciences and Public Health 2, no. 2: 28–31.
-
- Ali, S. , and Selim K.. 2018. “Bone and Soft Tissue Changes After Alveolar Ridge Preservation Using PRF Socket Plug Technique Versus Socket Plug Technique.” Egyptian Dental Journal 64: 3195–3208.
-
- Alrmali, A. , Saleh M. H., Mazzocco J., Zimmer J. M., Testori T., and Wang H. L.. 2023. “Auto‐Dentin Platelet‐Rich Fibrin Matrix Is an Alternative Biomaterial for Different Augmentation Procedures: A Retrospective Case Series Report.” Clinical and Experimental Dental Research 9, no. 6: 993–1004. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

