William F. House: The Father of Neurotology
- PMID: 39429272
- PMCID: PMC11490263
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.69724
William F. House: The Father of Neurotology
Abstract
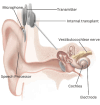
William F. House (1923-2012) was an ear, nose, and throat specialist with a particular focus in otology and an inventor, with perhaps his greatest invention being the single-channel cochlear implant. Although heavily criticized at the beginning of his career for developing the single-channel cochlear implant, many individuals would soon benefit from the device that House created. He also revolutionized a new technique for the removal of vestibular schwannomas with assistance from his neurosurgeon colleague, Dr. William Hitselberger. House is considered as the "Father of Neurotology" because of his many advancements in the medical field with refined surgery techniques and life-changing devices.
Keywords: cochlear implant; historical vignette; medical biographies; medical device innovator; neurotology; pioneer in medicine; william house.
Copyright © 2024, Goins et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures


References
-
- The early history of the cochlear implant: a retrospective. Mudry A, Mills M. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013;139:446–453. - PubMed
-
- House House, W. F. (2011a, August 29) Interview with William House, M.D. . [ Jul; 2024 ]. 2011. https://www.audiologyonline.com/interviews/interview-with-william-house-... https://www.audiologyonline.com/interviews/interview-with-william-house-...
-
- A winning team: William F. House, MD, and William E. Hitselberger, MD - online exclusive. AAO-HNS Bulletin. Bulletin-The official content hub of the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. [ Jul; 2024 ]. 2014. https://bulletin.entnet.org/home/article/21246213/a-winning-team-william... https://bulletin.entnet.org/home/article/21246213/a-winning-team-william...
-
- In memoriam: William F. House, DDS, MD, the “father of neurotology” (1923-2012) Berliner K. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013 - PubMed
-
- File:William F. Wikimedia Commons, William F. House, MD. [ Jul; 2024 ]. 2015. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:William_F._House,_M.D.jpg https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:William_F._House,_M.D.jpg
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
