Cutaneous Basal Cell Carcinoma In Situ: A Review of the World Literature
- PMID: 39429413
- PMCID: PMC11489863
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.69691
Cutaneous Basal Cell Carcinoma In Situ: A Review of the World Literature
Abstract
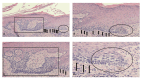
Cutaneous basal cell carcinoma (BCC) in situ is a recently recognized subtype of the skin neoplasm in which the abnormal cells are confined to the epidermis. BCC in situ of the skin was previously referred to as a superficial BCC. A review of the world literature has revealed 10 cutaneous BCCs in situ that have been described in nine patients but likely reflect a more general phenomenon. The neoplasm typically presents as an asymptomatic red plaque on the abdomen, upper extremity, back, and chest. Pathologic changes frequently show confluent tumor cells along the epidermal basal layer or superficial aggregates of neoplastic cells that are contiguous with the epidermis and extend into the dermis. Genomic evaluation has been performed in neoplasms from one individual with cutaneous BCC in situ and metastatic BCC; like other variants of BCC, an aberration of the PTCH1 gene was observed. In contrast to his liver metastasis, the in situ carcinoma had a lower tumor mutational burden, lacked programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and programmed death-ligand 2 (PD-L2) amplification and had a distinct PTCH1 mutation, suggesting that the in situ BCC of his skin and the metastatic BCC of his liver were derived from different clones of cells.
Keywords: basal; cancer; carcinoma; cell; cutaneous; fibroepithelioma; in situ; invasive; molecular; skin.
Copyright © 2024, Cohen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: Razelle Kurzrock declare(s) personal fees from Genentech, Merck Serono, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, TopAlliance, Takeda, Incyte, Debiopharm, Medimmune, Sequenom, Foundation Medicine, Konica Minolta, Grifols, Omniseq, and Guardant. Razelle Kurzrock has received research funding from these companies. Razelle Kurzrock declare(s) personal fees from X-Biotech, Caris, Datar Cancer Genomics, Neomed, Pfizer, Actuate Therapeutics, and Roche, . Razelle Kurzrock has been a consultant and/or speaker fees and/or advisory board of these companies. Razelle Kurzrock declare(s) non-financial support from IDbyDNA and CureMatch Inc. Razelle Kurzrock has an equity interest in these companies. Razelle Kurzrock declare(s) non-financial support from CureMatch and CureMetrix. Razelle Kurzrock serves on the Board of CureMatch and CureMetrix, and is a co-founder of CureMatch. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
