A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing STREAMLINE Canaloplasty to Trabecular Micro-Bypass Stent Implantation in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma
- PMID: 39429442
- PMCID: PMC11491083
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S481945
A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing STREAMLINE Canaloplasty to Trabecular Micro-Bypass Stent Implantation in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma
Abstract
Purpose: To report interim results of the VENICE study, a multi-center, randomized, controlled trial (RCT) comparing STREAMLINE Surgical System (STREAMLINE) canaloplasty with iStent inject W (iStent W) implantation in patients with mild-to-moderate primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) undergoing phacoemulsification.
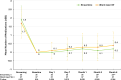
Patients and methods: Safety and efficacy analyses involving the first 72 randomized eyes are included in this report. Following pre- (Screening) and post-medication washout (Eligibility) visits, one eye per subject was randomized 1:1 to STREAMLINE or iStent W after undergoing uncomplicated phacoemulsification. Subjects were evaluated postoperatively at Day 1, Week 1, Month 1, 3, and 6. Intraocular pressure (IOP) measurements, number of IOP-lowering medications, and adverse events (AEs) were assessed at each follow-up visit.
Results: Seventy-two eyes were randomized; 35 underwent STREAMLINE canaloplasty and 37 were implanted with the iStent W. Seventy eyes completed their 6-month follow-up. Both the mean morning post-washout Baseline IOP between STREAMLINE 24.86±3.05 mmHg and iStent W 25.16±3.41 mmHg and the mean IOP at 6 months between STREAMLINE eyes 16.52±3.63 mmHg and iStent W eyes 16.08±3.19 mmHg were not statistically significantly different (p=0.691 and 0.596, respectively). At 6 months, more eyes were on zero glaucoma medications in the STREAMLINE group (81.8%) compared to the iStent W group (78.4%). In medication-free eyes, the mean IOP was reduced from 24.80±2.79 mmHg to 16.00±3.40 mmHg and 24.60±3.18 mmHg to 15.80±2.21 mmHg in the STREAMLINE and iStent W groups, respectively (p=0.752). Both groups showed reduction in IOP-lowering medications at every visit, compared to pre-washout (Screening), with STREAMLINE resulting in numerically fewer medications 0.20±0.48 compared to iStent W 0.40±0.79 at 6 months (P=0.384). AEs were mild and self-limited.
Conclusion: To our knowledge, the VENICE trial is the first RCT involving canaloplasty. These interim findings demonstrated comparable IOP and medication reduction between STREAMLINE canaloplasty and iStent W implantation, when combined with phacoemulsification.
Keywords: MIGS; POAG; STREAMLINE; canaloplasty; iStent inject W; microinvasive glaucoma surgery; primary open-angle glaucoma.
© 2024 Goldberg et al.
Conflict of interest statement
EMI, HR, and MH are employees of New World Medical. Inc. and participated in the design and conduct of the study, the collection, management, and analysis of data, and the preparation of the manuscript. DFG has financial interests and/or receives consulting fees with New World Medical, Glaukos, AbbVie, Alcon, Johnson & Johnson and Ocular Science. CO receives consulting fees from New World Medical. BEF receives consulting from New World Medical, Glaukos, Alcon, Sight Sciences, iStar Medical, Iantrek and Sanoculis, and research grants from NiCox; IPS receives consulting, research and/or speaker fees from New World Medical, Glaukos, AVG, Alcon, Allergan, B+L, Elios, IStar Medical, Lumibird, Nova Eye, Ocular Therapeutix, Radius, Rayner, Sight Sciences, Tarsus and Thea. LKS receives consulting fees from New World Medical, Allergan and Oculus Surgical. MKE receives research support from New World Medical and Glaukos. MYK is a consultant to New World Medical and his university receives fees on his behalf for this consultancy. MYK also has a patent (No. 10,729,584) related to the STREAMLINE Surgical System technology and a patent (US 2021/0322218 A1) owned by New World Medical. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Bourne RRA, Jonas JB, Friedman D; Vision Loss Expert Group of the Global Burden of Disease Study; GBD. Blindness and vision impairment collaborators. Global estimates on the number of people blind or visually impaired by glaucoma: a meta-analysis from 2000 to 2020. Eye. 2024;11:2036. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 38565601. doi:10.1038/s41433-024-02995-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Heijl A, Leske MC, Bengtsson B, Hyman L, Bengtsson B, Hussein M. early manifest glaucoma trial group. Reduction Intraocular Pres Glaucoma Progres Arch Ophthalmol. 2002;120(10):1268–1279. - PubMed
-
- Sun Y, Chen A, Zou M, et al.. Time trends, associations and prevalence of blindness and vision loss due to glaucoma: an analysis of observational data from the global burden of disease study 2017. BMJ Open. 2022;12(1):e053805. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-053805 PMID: 34992115; PMCID: PMC8739070. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

