Monoenergetic reconstructions and iodine density maps for visualization of coronary artery stents using 8-cm dual-layer detector spectral computed tomography: an in vitro phantom study
- PMID: 39429615
- PMCID: PMC11485354
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-24-786
Monoenergetic reconstructions and iodine density maps for visualization of coronary artery stents using 8-cm dual-layer detector spectral computed tomography: an in vitro phantom study
Abstract
Background: The effectiveness of coronary computed tomography (CT) angiography in assessing stent restenosis is hindered by heavy metal artifacts. This study aimed to evaluate the image quality of monoenergetic reconstructions and iodine density map for coronary stent imaging using an 8-cm dual-layer detector spectral CT.
Methods: In this study, 8 stents with a diameter <3 mm (group A) and 10 with a diameter ≥3 mm (group B) were placed in plastic tubes filled with iodinated contrast media and scanned. The internal diameter of the prepared stents was then measured by intravascular ultrasound. The reconstructed images included iodine density maps, conventional images, and different energy levels. The visualization of the stent lumen and stent structure was subjectively assessed using a 4-point Likert scale. The objective evaluation was performed using the in-stent lumen signal-to-noise ratio (SNRis), non-stent lumen SNR (SNRns), internal diameter difference (IDD), and blooming artifact index (BAI). The Friedman test and analysis of variance were used for multiple comparisons.
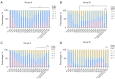
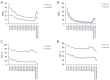
Results: For lumen visualization, the optimal monoenergetic images received the highest score for both group A (2.56±0.51) and group B (3.1±0.55). Multiple comparisons showed that there were significant differences between the optimal monoenergetic images and iodine density maps. However, for stent structure, iodine density maps received the highest score for group A (3.0±0.52) and group B (3.8±0.41). For quantitative assessment, the optimal monoenergetic images had the highest SNRis and SNRns, while the iodine density maps had the lowest SNRis and SNRns. For IDD and BAI, the iodine density maps yielded the smallest value.
Conclusions: The monoenergetic images on the second-generation dual-layer detector CT provide better visualization of the lumen and higher SNR. However, iodine density maps are superior for evaluating stent structure and IDD and BAI compared to monoenergetic and conventional reconstructions.
Keywords: Computed tomography (CT); coronary artery disease; dual-layer detector; in-stent restenosis; stent.
2024 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://qims.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/qims-24-786/coif). N.P. reports being a full-time employee of Bayer Healthcare Company during the conduct of the study. S.D. and Y.Z. report being full-time employees of Philips Healthcare during the conduct of the study. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Park SJ, Ahn JM, Kang DY, Yun SC, Ahn YK, Kim WJ, et al. Preventive percutaneous coronary intervention versus optimal medical therapy alone for the treatment of vulnerable atherosclerotic coronary plaques (PREVENT): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2024;403:1753-65. 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00413-6 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
