KIF15 promotes human glioblastoma progression under the synergistic transactivation of REST and P300
- PMID: 39430242
- PMCID: PMC11488581
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.98668
KIF15 promotes human glioblastoma progression under the synergistic transactivation of REST and P300
Abstract
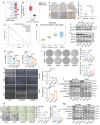
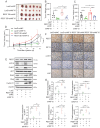
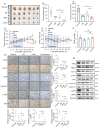
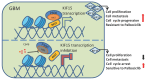
Glioblastoma (GBM) is highly invasive and lethal. The failure to cure GBM highlights the necessity of developing more effective targeted therapeutic strategies. KIF15 is a motor protein to be involved in cell mitosis promotion, cell structure assembly and cell signal transduction. The precise biological function and the potential upstream regulatory mechanisms of KIF15 in GBM remain elusive. Here, we demonstrated that KIF15 was abnormally up-regulated in GBM and predicted poor prognosis of GBM patients. KIF15 promotes GBM cell proliferation, metastasis and cell cycle progression. REST could bind to KIF15 promoter and transactivate KIF15. Furthermore, REST interacts with P300 and depends on its histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity to co-regulate KIF15 expression. Both REST and P300 were highly expressed in GBM and predicted poor prognosis of GBM patients alone or in combination with KIF15. The tumorigenic function of KIF15 in GBM was regulated by REST in vitro and in vivo and the combinational treatment of cell cycle inhibitor Palbociclib with P300 HAT inhibitor inhibited GBM xenografts survival more significantly. Our findings indicate that KIF15 promotes GBM progression under the synergistic transactivation of REST and P300. P300/REST/KIF15 signaling axis is expected to be served as a cascade of candidate therapeutic targets in anti-GBM.
Keywords: Acetylation; Glioblastoma (GBM); KIF15; P300; REST.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




References
-
- Thomas DL. 2021 updates to the World Health Organization classification of adult-type and pediatric-type diffuse gliomas: a clinical practice review. Chinese clinical oncology. 2023;12:7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

