Improving antibiotic prescribing - Recommendations for funding and pricing policies to enhance use of point-of-care tests
- PMID: 39430908
- PMCID: PMC11488418
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hpopen.2024.100129
Improving antibiotic prescribing - Recommendations for funding and pricing policies to enhance use of point-of-care tests
Abstract
Introduction: Diagnostics can contribute to the improved quality of antibiotic prescribing. However, there is potential to enhance the use of point-of-care tests (POCTs) in general practice. This paper presents fit-for-purpose policy recommendations related to funding and pricing for POCTs applied for community-acquired acute respiratory tract infections (CA-ARTIs).
Methods: The development of the recommendations was informed by an analysis of the current status of funding and pricing policy frameworks for CA-ARTI POCTs in European countries, and an identification of barriers and facilitators for their uptake. Draft recommendations were developed and subsequently revised based on written and verbal feedback from meetings with experts.
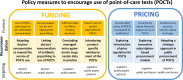
Results: The proposal includes four recommendations for policy interventions related to funding and three recommendations regarding pricing policies. Two of the funding policy-related recommendations concern physicians' remuneration, and two relate to product-specific reimbursement (public coverage) of the CA-ARTI POCTs. The pricing-related recommendations include a proposal to explore the introduction of price regulation, to pilot subscription-fee procurement models and to enhance more strategic approaches in public procurement of CA-ARTI POCTs.
Conclusions: Optimised pricing and funding policies could make a difference in enhancing uptake of CA-ARTI POCTs. It is crucial for the successful implementation of policies to consider country settings. Additionally, supportive policy action is recommended, including the systematic use of health technology assessment, stakeholder communication, and monitoring and evaluation.
Keywords: Antibiotic prescribing; Community-acquired acute respiratory tract infections; Diagnostic; Funding; Point-of-care test; Pricing.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessing, Pricing and Funding Point-of-Care Diagnostic Tests for Community-Acquired Acute Respiratory Tract Infections-Overview of Policies Applied in 17 European Countries.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Jul 22;11(8):987. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11080987. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35892377 Free PMC article.
-
Stakeholders' views and experiences on implementing new diagnostics in primary care to support management of community-acquired acute respiratory tract infections: a qualitative study.Front Public Health. 2023 Jul 31;11:1216940. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1216940. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37583883 Free PMC article.
-
Barriers and Facilitators in Pricing and Funding Policies of European Countries That Impact the Use of Point-of-Care Diagnostics for Acute Respiratory Tract Infections in Outpatient Practices.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Dec 4;13(23):3596. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13233596. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38066837 Free PMC article.
-
Pricing, Procurement and Reimbursement Policies for Incentivizing Market Entry of Novel Antibiotics and Diagnostics: Learnings from 10 Countries Globally.Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2024 Sep;22(5):629-652. doi: 10.1007/s40258-024-00888-y. Epub 2024 Jun 5. Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2024. PMID: 38837100 Review.
-
Implementation of medicines pricing policies in sub-Saharan Africa: systematic review.Syst Rev. 2022 Dec 1;11(1):257. doi: 10.1186/s13643-022-02114-z. Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36457058 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O'Neill J. Tackling drug-resistant infections globally: final report and recommendations. London, 2016. Available from: http://www.advancedinvestor.com/resources/Research-Materials/Disease/UK_... (acccessed 25 May 2023).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources