The Netrod™ six-electrode radiofrequency renal denervation system for uncontrolled hypertension: a sham-controlled trial
- PMID: 39431289
- PMCID: PMC11578641
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehae703
The Netrod™ six-electrode radiofrequency renal denervation system for uncontrolled hypertension: a sham-controlled trial
Keywords: Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring; Hypertension; Renal denervation.
Figures
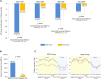
References
-
- Townsend RR, Mahfoud F, Kandzari DE, Kario K, Pocock S, Weber MA, et al. Catheter-based renal denervation in patients with uncontrolled hypertension in the absence of antihypertensive medications (SPYRAL HTN-OFF MED): a randomised, sham-controlled, proof-of-concept trial. Lancet 2017;390:2160–70. 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32281-X - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kandzari DE, Böhm M, Mahfoud F, Townsend RR, Weber MA, Pocock S, et al. Effect of renal denervation on blood pressure in the presence of antihypertensive drugs: 6-month efficacy and safety results from the SPYRAL HTN-ON MED proof-of-concept randomised trial. Lancet 2018;391:2346–55. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30951-6 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

