Implementing geriatric assessment for dose optimization of CDK4/6 inhibitors in older breast cancer patients
- PMID: 39431459
- PMCID: PMC11572072
- DOI: 10.1080/14796694.2024.2413841
Implementing geriatric assessment for dose optimization of CDK4/6 inhibitors in older breast cancer patients
Abstract
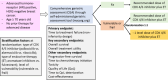
Current evidence from both randomized trials and real-world studies suggests that older patients with advanced hormone receptor-positive/HER2-negative (HR+/HER2) breast cancer derive clinical benefit from the addition of CDK4/6 inhibitors to endocrine therapy. However, a higher risk for adverse events due to CDK4/6 inhibitors among older patients is evident, leading to a trend of initiating CDK4/6 inhibitors at lower dose in clinical practice, though without evidence. The aim of the IMPORTANT-trial, a pragmatic, multinational, open-label, partly decentralized randomized trial is to investigate whether lower starting dose of CDK4/6 inhibitors combined with endocrine therapy is comparable to full dose in older (≥70 years old) patients with advanced HR+/HER2- breast cancer who are assessed as vulnerable or frail based on comprehensive geriatric assessment.Clinical Trial Registration: NCT06044623 (ClinicalTrials.gov); Registration date: 13 September 2023.
Keywords: CDK4/6 inhibitors; advanced breast cancer; comprehensive geriatric assessment; lower dose; randomized.
Plain language summary
[Box: see text].
Conflict of interest statement
A Valachis has received unrestricted research grant from Roche and MSD unrelated to current research project. P Karihtala has been an investigator in studies funded by Lilly, Novartis and Pfizer and has been involved in the advisory boards of Lilly, Novartis and Pfizer. I Meattini declares advisory board participation supported by Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Astra Zeneca, Novartis, Gilead, Menarini StemLine, SeaGen, Daiichi Sankyo. L Biganzoli has received honoraria from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Exact Sciences, Gilead, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Roche, Sanofi, SeaGen and unrestricted research grant from Celgene, Genomic Health, Novartis unrelated to current research project. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
References
-
- Li J, Huo X, Zhao F, et al. . Association of cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 inhibitors with survival in patients with hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3:e2020312. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.20312 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Singh H, Kanapuru B, Smith C, et al. . FDA analysis of enrollment of older adults in clinical trials for cancer drug registration: a 10-year experience by the US Food and Drug Administration. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(Suppl. 15):e10009. doi:10.1200/JCO.2017.35.15_suppl.10009 - DOI
-
- Howie LJ, Singh H, Bloomquist E, et al. . Outcomes of older women with hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-negative metastatic breast cancer treated with a cdk4/6 inhibitor and an aromatase inhibitor: an FDA pooled analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37:3475–3483. doi:10.1200/JCO.18.02217 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pulido M, Brain E, Falandry C, et al. . PALOMAGE, a French real-world cohort of elderly women beyond age 70 with advanced breast cancer receiving palbociclib: baseline characteristics and safety evaluation. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39:1012. doi:10.1200/JCO.2021.39.15_suppl.1012 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous