Unveiling exosomes: Cutting-edge isolation techniques and their therapeutic potential
- PMID: 39431552
- PMCID: PMC11492151
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.70139
Unveiling exosomes: Cutting-edge isolation techniques and their therapeutic potential
Abstract
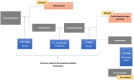
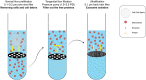
Exosomes are one type of nanosized membrane vesicles with an endocytic origin. They are secreted by almost all cell types and play diverse functional roles. It is essential for research purposes to differentiate exosomes from microvesicles and isolate them from other components in a fluid sample or cell culture medium. Exosomes are important mediators in cell-cell communication. They deliver their cargos, such as mRNA transcripts, microRNA, lipids, cytosolic and membrane proteins and enzymes, to target cells with or without physical connections between cells. They are highly heterogeneous in size, and their biological functions can vary depending on the cell type, their ability to interact with recipient cells and transport their contents, and the environment in which they are produced. This review summarized the recent progress in exosome isolation and characterization techniques. Moreover, we review the therapeutic approaches, biological functions of exosomes in disease progression, tumour metastasis regulation, immune regulation and some ongoing clinical trials.
Keywords: cancer therapy; characterization; exosome; immune modulation; isolation.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Pan B‐T, Johnstone RM. Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: selective externalization of the receptor. Cell. 1983;33(3):967‐978. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

