Trends in NHANES Biomonitored Exposures in California and the United States following Enactment of California's Proposition 65
- PMID: 39432449
- PMCID: PMC11493239
- DOI: 10.1289/EHP13956
Trends in NHANES Biomonitored Exposures in California and the United States following Enactment of California's Proposition 65
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of toxic chemicals in US commerce has prompted some states to adopt laws to reduce exposure. One with broad reach is California's Proposition 65 (Prop 65), which established a list of chemicals that cause cancer, developmental harm, or reproductive toxicity. The law is intended to discourage businesses from using these chemicals and to minimize consumer exposure. However, a key question remains unanswered: Has Prop 65 reduced population-level exposure to the listed chemicals?
Objective: We used national biomonitoring data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to evaluate the impact of Prop 65 on population-level exposures.
Methods: We evaluated changes in blood and urine concentrations of 37 chemicals (including phthalates, phenols, VOCs, metals, PAHs, and PFAS), among US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) participants in relation to the time of chemicals' Prop 65 listing. Of these, 11 were listed prior to, 11 during, and 4 after the biomonitoring period. The remaining 11 were not listed but were closely related to a Prop 65-listed chemical. Where biomonitoring data were available from before and after the date of Prop 65 listing, we estimated the change in concentrations over time for Californians compared with non-Californians, using a difference-in-differences model. We used quantile regression to estimate changes in exposure over time, as well as differences between Californians and non-Californians at the 25th, 75th, and 95th percentiles.
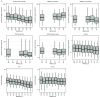
Results: We found that concentrations of biomonitored chemicals generally declined nationwide over time irrespective of their inclusion on the Prop 65 list. Median bisphenol A (BPA) concentrations decreased 15% after BPA's listing on Prop 65, whereas concentrations of the nonlisted but closely related bisphenol S (BPS) increased 20% over this same period, suggesting chemical substitution. Californians generally had lower levels of biomonitored chemicals than the rest of the US population.
Discussion: Our findings suggest that increased scientific and regulatory attention, as well as public awareness of the harms of Prop 65-listed chemicals, prompted changes in product formulations that reduced exposure to those chemicals nationwide. Trends in bisphenols and several phthalates suggest that manufacturers replaced some listed chemicals with closely related but unlisted chemicals, increasing exposure to the substitutes. Our findings have implications for the design of policies to reduce toxic exposures, biomonitoring programs to inform policy interventions, and future research into the regulatory and market forces that affect chemical exposure. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP13956.
Figures




References
-
- US EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency). 2023. TSCA Chemical Substance Inventory. https://www.epa.gov/tsca-inventory/how-access-tsca-inventory [accessed 22 August 2023].
-
- Safe Drinking Water and Toxic Enforcement Act of 1986. 1986. Cal. Health and Safety Code. Vol. 25249 -25249.14.
-
- Pease WS. 1991. Chemical hazards and the public’s right to know. Environment 33(10):12–20, 10.1080/00139157.1991.9932550. - DOI
-
- California OEHHA (Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment). n.d. How chemicals are added to the Proposition 65 list. https://oehha.ca.gov/proposition-65/how-chemicals-are-added-proposition-... [accessed 31 December 2021].

