Torque teno virus: a potential marker of immune reconstitution in youths with vertically acquired HIV
- PMID: 39433755
- PMCID: PMC11494008
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-73870-2
Torque teno virus: a potential marker of immune reconstitution in youths with vertically acquired HIV
Abstract
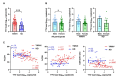
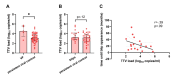
Torque teno virus (TTV) viral load (VL), a component of the human virome, increases during immune suppression or dysregulation. This study aimed to explore TTV VL in youths living with vertically acquired HIV (YWVH) and its potential as an immunovirological marker. We performed an observational, retrospective study involving YWVH under antiretroviral treatment (ART) from the Spanish Cohort of HIV-infected children, adolescents, and vertically HIV-infected patients transferred to Adult Units (CoRISpe-FARO), compared to HIV-negative healthy donors (HD). Plasma TTV VL was assessed by qPCR. T-cell phenotype was analysed on cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cells by flow cytometry. Correlations with baseline CD4 and CD8 and long-term virological evolution were examined. A total of 57 YWVH were compared with 23 HD. YWVH had a median CD4 T-cells of 736 cells/mm3 [IQR: 574-906], a median of 17 years [IQR: 14-20.5] since ART initiation, and 65 months [IQR: 39-116] under HIV-RNA virological control. TTV VL was higher among YWVH and in males compared with females (p < 0.05). Among YWVH, TTV VL correlated with CD4 and CD8 counts and the CD4/CD8 ratio (p = 0.002; r = - 0.39, p = 0.037; r = 0.277, p = 0.005; r = - 0.37 respectively). TTV VL correlated with activation expression markers (HLA-DR+/CD38+) on CD4 (p = 0.007, r = 0.39) and the soluble proinflammatory cytokine IL-6 (p = 0.006, r = 0.38).
Keywords: Antiretroviral treatment; CD4/CD8 ratio; Immune reconstitution; TTV; Youths with vertically acquired HIV.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Focosi, D., Antonelli, G., Pistello, M. & Maggi, F. Torquetenovirus: The human virome from bench to bedside. Clin. Microbiol. Infect.22, 589–593 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Solis, M. et al. Torquetenovirus viremia for early prediction of graft rejection after kidney transplantation. J. Infect.79, 56–60 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Sawata, T. et al. Clinical significance of changes in Torque Teno virus DNA titer after chemotherapy in patients with primary lung cancer. Respir Investig.56, 173–178 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CB21/13/00025/Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Infecciosas-ISCIII (CIBERINFEC)
- CB21/13/00077/Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Infecciosas-ISCIII (CIBERINFEC)
- CB21/13/00044/Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Infecciosas-ISCIII (CIBERINFEC)
- CP23/00009/Instituto de Salud Carlos III (ISCIII). Miguel Servet Program
- CB22/01/00041/Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Bioingeniería, Biomateriales y Nanomedicina (CIBER-BBN)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

