Glutamine sensing licenses cholesterol synthesis
- PMID: 39433901
- PMCID: PMC11612431
- DOI: 10.1038/s44318-024-00269-0
Glutamine sensing licenses cholesterol synthesis
Abstract
The mevalonate pathway produces essential lipid metabolites such as cholesterol. Although this pathway is negatively regulated by metabolic intermediates, little is known of the metabolites that positively regulate its activity. We found that the amino acid glutamine is required to activate the mevalonate pathway. Glutamine starvation inhibited cholesterol synthesis and blocked transcription of the mevalonate pathway-even in the presence of glutamine derivatives such as ammonia and α-ketoglutarate. We pinpointed this glutamine-dependent effect to a loss in the ER-to-Golgi trafficking of SCAP that licenses the activation of SREBP2, the major transcriptional regulator of cholesterol synthesis. Both enforced Golgi-to-ER retro-translocation and the expression of a nuclear SREBP2 rescued mevalonate pathway activity during glutamine starvation. In a cell model of impaired mitochondrial respiration in which glutamine uptake is enhanced, SREBP2 activation and cellular cholesterol were increased. Thus, the mevalonate pathway senses and is activated by glutamine at a previously uncharacterized step, and the modulation of glutamine synthesis may be a strategy to regulate cholesterol levels in pathophysiological conditions.
Keywords: Cholesterol; HMGCR; MFN2; Nutrient Sensing; SREBP2.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. BMG and LP are inventors on a European patent application (No. EP23171736.4) filed by the Max-Planck-Gesellschaft. The patent application covers the use of GLUL activators or inhibitors to modulate lipid levels. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


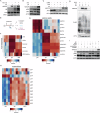
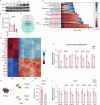
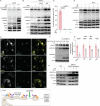
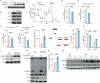
References
-
- Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917 - PubMed
-
- Boncompain G, Divoux S, Gareil N, de Forges H, Lescure A, Latreche L, Mercanti V, Jollivet F, Raposo G, Perez F (2012) Synchronization of secretory protein traffic in populations of cells. Nat Methods 9:493–498 - PubMed
-
- Bray NL, Pimentel H, Melsted P, Pachter L (2016) Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nat Biotechnol 34:525–527 - PubMed
-
- Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1997) The SREBP pathway: regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell 89:331–340 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ERC-StG-2019 852457/EC | European Research Council (ERC)
- Project ID 269925409/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- 411422114-GRK 2550/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- NWO; 016.176.643/Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research
- M.22.034; GENESIS/Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research

