Current understanding of the impact of United States military airborne hazards and burn pit exposures on respiratory health
- PMID: 39434148
- PMCID: PMC11492460
- DOI: 10.1186/s12989-024-00606-5
Current understanding of the impact of United States military airborne hazards and burn pit exposures on respiratory health
Abstract
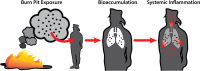
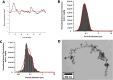
Millions of United States (U.S.) troops deployed to the Middle East and Southwest Asia were exposed to toxic airborne hazards and/or open-air burn pits. Burn pit emissions contain particulate matter combined with toxic gasses and heavy metals. Ongoing research has demonstrated that exposures to the airborne hazards from military burn pits have profound and lasting health and wellness consequences. Research on the long-term health consequences of exposure to open burn pits has been limited. Work continues to understand the scope of the health impacts and the underlying pathobiology following exposures and to establish care standards. The U.S. Sergeant First Class Heath Robinson Honoring our Promise to Address Comprehensive Toxics (PACT) Act was signed into law August 2022. This act expands the benefits and services to U.S. Veterans exposed to toxicants, requires the Veterans Health Administration to provide toxic exposure screening, and supports increased research, education, and treatment due to toxic occupational exposures. This review highlights the state of the science related to military burn pit exposures research with an emphasis on pulmonary health. Clinical data demonstrate areas of reduced or delayed pulmonary ventilation and lung pathologies such as small airways scarring, diffuse collagen deposition and focal areas of ossification. Identification and characterization of foreign matter deposition in lung tissues are reported, including particulate matter, silica, titanium oxides, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. These data are consistent with toxic exposures and with the symptoms reported by post-deployment Veterans despite near-normal non-invasive pulmonary evaluations. On-going work toward new methods for non-invasive pulmonary diagnoses and disease monitoring are described. We propose various studies and databases as resources for clinical and health outcomes research. Pre-clinical research using different burn pit modeling approaches are summarized, including oropharyngeal aspiration, intranasal inhalation, and whole-body exposure chamber inhalation. These studies focus on the impacts of specific toxic substances as well as the effects of short-term and sustained insults over time on the pulmonary systems.
Keywords: Airborne hazards; Burn Pits 360; Burn pit; Implementation; Inflammation; Inhalation; Military; PACT Act; Pulmonary; Veterans.
© 2024. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- American Public Health Association. Cleanup of U.S. military burn pits in Iraq and Afghanistan. American Public Health Association; 2015.
-
- National Academies of Sciences E Medicine. Assessment of the department of veterans affairs airborne hazards and open burn pit registry. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press; 2017. - PubMed
-
- US Department of Defense. Exposure to toxins produced by burn pits: congressional data request and studies. 2011.
-
- Hoisington AJ, Stearns-Yoder KA, Kovacs EJ, Postolache TT, Brenner LA. Airborne exposure to pollutants and mental health: a review with implications for united states veterans. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2024. 10.1007/s40572-024-00437-8. - PubMed
-
- Perveen MM, Mayo-Malasky HE, Lee-Wong MF, Tomaska JM, Forsyth E, Gravely A, et al. Gross hematuria and lower urinary tract symptoms associated with military burn pits exposures in us veterans deployed to Iraq and Afghanistan. J Occup Environ Med. 2023;65(9):740–4. 10.1097/jom.0000000000002919. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

