Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma of prostate combined with prostatic abscess in an adult patient: a case report and literature review
- PMID: 39434757
- PMCID: PMC11491222
- DOI: 10.21037/tau-24-117
Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma of prostate combined with prostatic abscess in an adult patient: a case report and literature review
Abstract
Background: Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS) of the prostate is a rare and aggressive malignant tumor in adults with a poor prognosis in general. The main presenting symptoms are dysuria and acute urinary retention. Prostate ERMS is easily misdiagnosed, which leads to delays in treatment.
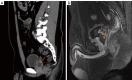
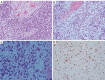
Case description: We report the case of a previously healthy 31-year-old man who presented with dysuria for 3 months. Digital rectal examination (DRE), ultrasound, and computed tomography (CT) were suggestive of the possibility of a 2.0 cm × 3.0 cm abscess in the left lobe of the prostate. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) was at a normal level, and C-reactive protein (CRP) concentration was elevated. The patient underwent surgical drainage by transurethral incision of the prostatic abscess. There was a significant improvement in the maximal urinary flow rate on postoperative day 5. However, the patient presented with acute urinary retention again on the 20th postoperative day. DRE and pelvic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed a recurrence of an enlarged mass in the left lobe of the prostate. PSA level was again normal. Cystoscopy revealed a large neoplasm arising from the prostate obstructing the bladder outlet, and a diagnostic transurethral resection of this prostate tumor was performed. Histopathology revealed the mass to be an embryonic rhabdomyosarcoma. Subsequently, the patient was transferred to the Oncology Department and received chemoradiotherapy. After chemoradiotherapy, the size of the prostate became normal. Unfortunately, the patient deteriorated rapidly and eventually succumbed to multiple organ failure 1 year after the initial presentation.
Conclusions: Due to its non-specific presenting symptoms, prostate ERMS can be easily misdiagnosed, which can lead to treatment delay. Multimodality approaches, including neoadjuvant/adjuvant chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and radical resection, can improve the survival rate and reduce ERMS patient mortality.
Keywords: Case report; chemoradiotherapy; embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS); prostatic abscess.
2024 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tau.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tau-24-117/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma of the prostate in a young male: A rare case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2023 May;106:108228. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2023.108228. Epub 2023 Apr 18. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37086503 Free PMC article.
-
More advantages in detecting bone and soft tissue metastases from prostate cancer using 18F-PSMA PET/CT.Hell J Nucl Med. 2019 Jan-Apr;22(1):6-9. doi: 10.1967/s002449910952. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Hell J Nucl Med. 2019. PMID: 30843003
-
Perianal embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma: A case report.Oncol Lett. 2024 Aug 8;28(4):487. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14620. eCollection 2024 Oct. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39185492 Free PMC article.
-
Primary embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma of the prostate in adults: report of a case and review of the literature.Int J Surg Pathol. 2011 Dec;19(6):831-7. doi: 10.1177/1066896910395585. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Int J Surg Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21427103 Review.
-
De novo large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the prostate gland with pelvic lymph node metastasis: a case report with review of literature.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Dec 1;7(12):9061-6. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25674288 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
