Near-Infrared Driven Gold Nanoparticles-Decorated g-C3N4/SnS2 Heterostructure through Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapy for Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 39435043
- PMCID: PMC11492912
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S478883
Near-Infrared Driven Gold Nanoparticles-Decorated g-C3N4/SnS2 Heterostructure through Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapy for Cancer Treatment
Abstract
Background: Phototherapy based on photocatalytic semiconductor nanomaterials has received considerable attention for the cancer treatment. Nonetheless, intense efficacy for in vivo treatment is restricted by inadequate photocatalytic activity and visible light response.
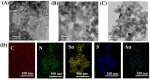
Methods: In this study, we designed a photocatalytic heterostructure using graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) and tin disulfide (SnS2) to synthesize g-C3N4/SnS2 heterostructure through hydrothermal process. Furthermore, Au nanoparticles were decorated in situ deposition on the surface of the g-C3N4/SnS2 heterostructure to form g-C3N4/SnS2@Au nanoparticles.
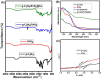
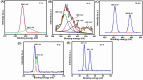
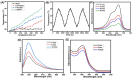
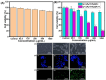
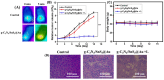
Results: The g-C3N4/SnS2@Au nanoparticles generated intense reactive oxygen species radicals under near-infrared (NIR) laser irradiation through photodynamic therapy (PDT) pathways (Type-I and Type-II). These nanoparticles exhibited enhanced photothermal therapy (PTT) efficacy with high photothermal conversion efficiency (41%) when subjected to 808 nm laser light, owing to the presence of Au nanoparticles. The in vitro studies have indicated that these nanoparticles can induce human liver carcinoma cancer cell (HepG2) apoptosis (approximately 80% cell death) through the synergistic therapeutic effects of PDT and PTT. The in vivo results demonstrated that these nanoparticles exhibited enhanced efficient antitumor effects based on the combined effects of PDT and PTT.
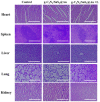
Conclusion: The g-C3N4/SnS2@Au nanoparticles possessed enhanced photothermal properties and PDT effect, good biocompatibility and intense antitumor efficacy. Therefore, these nanoparticles could be considered promising candidates through synergistic PDT/PTT effects upon irradiation with NIR laser for cancer treatment.
Keywords: Gold nanoparticles; Photodynamic therapy; Photothermal therapy; SnS2; g-C3N4.
© 2024 Dash et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Luo M, Yukawa H, Sato K, et al. Multifunctional magnetic CuS/Gd2O3 nanoparticles for fluorescence/magnetic resonance bimodal imaging-guided Photothermal-intensified Chemodynamic synergetic therapy of targeted tumors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(30):34365–34376. doi:10.1021/acsami.2c06503 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dash P, Thirumurugan S, Tseng CL, et al. Synthesis of Methotrexate-Loaded Dumbbell-Shaped Titanium Dioxide/Gold Nanorods Coated with Mesoporous Silica and Decorated with Upconversion Nanoparticles for Near-Infrared-Driven Trimodal Cancer Treatment. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023;15(28):33335–33347. doi:10.1021/acsami.3c04300 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

