Risk of type 2 diabetes after breast cancer treatment: a population-based cohort study in Denmark
- PMID: 39436974
- PMCID: PMC11884854
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djae261
Risk of type 2 diabetes after breast cancer treatment: a population-based cohort study in Denmark
Abstract
Purpose: Data on type 2 diabetes (T2D) risk after breast cancer (BC) could guide preventive strategies. Yet, studies had limitations regarding sample size, follow-up, and contemporary treatments. We evaluated the risk of T2D after BC overall, by cancer treatment, and compared with a matched cohort of cancer-free women.
Methods: We assembled a population-based cohort of early-stage BC patients aged 30 years or more diagnosed during 1996-2021 in Denmark. We created a comparison cohort of 5 cancer- and T2D-free women for each BC patient, matched 6 months after BC diagnosis date on age and region. We followed both cohorts until T2D diagnosis, emigration, death, or December 31, 2022. We computed 5-year cumulative incidences and used Cox models to calculate time-varying adjusted hazard ratios (aHR) of T2D.
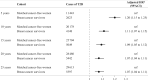
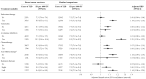
Results: Among 74 526 BC survivors and 372 630 matched cancer-free women, 5-year cumulative incidences of T2D were 3.8% (95% confidence interval [CI] = 3.7 to 3.9) and 3.3% (95% CI = 3.3 to 3.4), respectively. The aHR of T2D was elevated but attenuated over follow-up (aHR5-years = 1.20, 95% CI = 1.15 to 1.25, and aHR15-years = 1.09, 95% CI = 1.05 to 1.12). Adjuvant endocrine therapy (aHR = 1.14; 95% CI = 1.10 to 1.19), aromatase inhibitors (aHR = 1.25; 95% CI = 1.18 to 1.32), and less so tamoxifen (aHR = 1.05; 95% CI = 0.99 to 1.11), were associated with elevated risk of T2D in women with BC vs cancer-free women. Among BC patients, chemotherapy (aHR = 1.10, 95% CI = 1.03 to 1.17) and radiation therapy (right-sided aHR = 1.18, 95% CI = 1.09 to 1.27 and left-sided aHR = 1.24, 95CI = 1.15 to 1.33) were associated with increased T2D risk.
Conclusion: BC was associated with excess risk of T2D, although of lower magnitude than previously reported. The excess risk was temporary and related to BC treatment but could also be influenced by obesity and heightened T2D diagnostic activity.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The development of type 2 diabetes management in people with severe mental illness in the Capital Region of Denmark from 2001 to 2015.Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2024 Mar;149(3):219-233. doi: 10.1111/acps.13650. Epub 2024 Jan 6. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2024. PMID: 38183340
-
Mammographic density, endocrine therapy and breast cancer risk: a prognostic and predictive biomarker review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 26;10(10):CD013091. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013091.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34697802 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
-
Breast cancer and incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Nov;202(1):11-22. doi: 10.1007/s10549-023-07043-6. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 37656235 Free PMC article.
-
Hormonal therapies for early breast cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Jul;11(26):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-134. doi: 10.3310/hta11260. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17610808
References
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, et al.; IDF Diabetes Atlas Committee. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157:107843. - PubMed
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al.Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209-249. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

