Thioflavin-T: application as a neuronal body and nucleolar stain and the blue light photo enhancement effect
- PMID: 39438516
- PMCID: PMC11496653
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-74359-8
Thioflavin-T: application as a neuronal body and nucleolar stain and the blue light photo enhancement effect
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Thioflavin-T: application as a neuronal body and nucleolar stain and the blue light photo enhancement effect.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 20;14(1):30574. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82113-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39706912 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
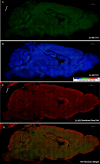
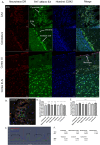
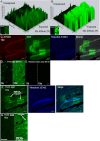
Thioflavin-T (THT) is a common and indispensable tool for the study of amyloid pathologies and protein aggregation, both in vitro and for histological samples. In this study we expand the use of THT beyond its canonical usage for staining amyloid plaques and demonstrate its novel use as an easy and rapid stain comparable to fluorescent Nissl staining, allowing for clear discernment of neuronal cell bodies and also nucleoli in fixed tissue and live cells. We believe that this is of value for any lab that studies central nervous system (CNS) tissues. Furthermore, we show that THT could potentially be used as a an alternative to the use of fluorescent reporters or other more costly RNA binding compounds in the study of nucleolar dynamics owing to its ability to clearly stain nucleoli in live cells. We also discovered the previously unreported effect of blue light exposure on the photo enhancement of THT excited by a 488 nm laser in stained tissue sample and how to avoid complications arising from this effect. Finally, we provide a simple protocol that can be easily adjusted either for using THT as a neuronal cell body and nucleoli stain, compatible with antibody based staining methods tested up to 4 fluorophores, or alternatively by using an additional washing step the protocol may be used for amyloid plaque detection in fixed brain tissue.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloid Beta; Brain; Neuron; Nissl; Photo Enhancement; Thioflavin-T.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Naiki, H., Higuchi, K., Hosokawa, M. & Takeda, T. Fluorometric determination of amyloid fibrils in vitro using the fluorescent dye, thioflavine T. Anal. Biochem. 177, 244–249 (1989). - PubMed
-
- Srivastava, A. et al. Identifying the bond responsible for the fluorescence modulation in an amyloid fibril sensor. Chemistry 16, 9257–9263 (2010). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

