MiR-21-3p inhibitor exerts myocardial protective effects by altering macrophage polarization state and reducing excessive mitophagy
- PMID: 39438580
- PMCID: PMC11496525
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-024-07050-3
MiR-21-3p inhibitor exerts myocardial protective effects by altering macrophage polarization state and reducing excessive mitophagy
Abstract
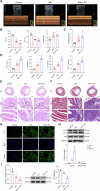
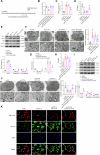
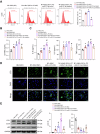
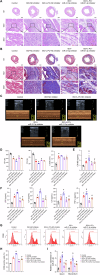
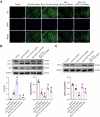
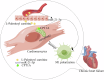
Chronic heart failure (CHF) is closely associated with inflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction in cardiomyocytes. This study attempts to investigate the effects of microRNA-21-3p (miR-21-3p) on macrophage polarization and mitophagy in CHF. Here we found miR-21-3p was upregulated in CHF and negatively correlated with carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1A (CPT1A). L-palmitoyl carnitine (L-PC) exacerbated isoproterenol (ISO)-induced myocardial structural disruption and fibrosis in rats, which was exacerbated by miR-21-3p. Mechanistically, miR-21-3p accelerated M1 macrophage polarization. Both miR-21-3p inhibitor and CPT1A overexpression suppressed mitophagy. The inhibition of CPT1A on mitophagy was reversed by miR-21-3p. MiR-21-3p targeted CPT1A mRNA and co-localized with CPT1A protein in cardiomyocytes. In the co-culture system of M1 macrophages and H9c2 cells, miR-21-3p mimics in H9c2 cells promoted M1 polarization, whereas miR-21-3p inhibitor reduced M1 phenotype. M1 macrophages exacerbated H9c2 cell damage. These findings support the potential therapeutic targeting of miR-21-3p to regulate inflammation and mitophagy by inducing CPT1A in CHF.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Zhang, Y. et al. Propofol compared with sevoflurane general anaesthesia is associated with decreased delayed neurocognitive recovery in older adults. Br. J. Anaesth.121, 595–604 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Frangogiannis, N. G. Cardiac fibrosis: cell biological mechanisms, molecular pathways and therapeutic opportunities. Mol. Asp. Med.65, 70–99 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

