Evaluation of the Steno Type 1 Risk Engine in predicting cardiovascular events in an ethnic mixed population of type 1 diabetes mellitus and its association with chronic microangiopathy complications
- PMID: 39438880
- PMCID: PMC11515709
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-024-02460-3
Evaluation of the Steno Type 1 Risk Engine in predicting cardiovascular events in an ethnic mixed population of type 1 diabetes mellitus and its association with chronic microangiopathy complications
Abstract
Background: The Steno Type 1 Risk Engine (ST1RE) was developed to aid clinical decisions in primary prevention for individuals with type 1 diabetes (T1D), as existing cardiovascular (CV) risk models for the general population and type 2 diabetes tend to underestimate CV risk in T1D. However, the applicability of ST1RE in different populations remains uncertain, as prediction models developed for one population may not accurately estimate risk in another. This study aimed to evaluate the performance of the ST1RE in predicting CV events among ethnically mixed T1D individuals and its association with the progression of microangiopathy complications.
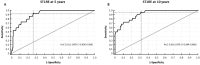
Methods: A retrospective survey of 435 adults with T1D who were free of CV events at baseline was assessed by ST1RE and chronic diabetes complications at 5 and 10 years of follow-up. The estimated CV risk rates were compared with the observed rates at 5 and 10 years using statistical analyses, including Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, Hosmer-Lemeshow test, Kaplan-Meier curves analysis and Cox-regression models.
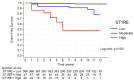
Results: Among 435 patients (aged 25 years; interquartile range [IQR]: 21-32) with a median T1D duration of 13 years (IQR: 9-18), only 5% were categorized into the high ST1RE group. Within a median follow-up of 9.2 years (IQR 6.0-10.7), 5.5% of patients experienced a CV event (1.6%, 14.9%, and 50% from the low, moderate, and high-risk groups, respectively). The hazard ratios (HRs) for CV events were greater in the high-risk group (HR 52.02; 95% CI 18.60-145.51, p < 0.001) and in the moderate-risk group (HR 8.66; 95% CI 2.90-25.80, p < 0.001) compared to the low-risk group. The ST1RE estimated CV events were similar to the observed at 5 years (3.4% vs. 3.5%; χ2 = 10.12, p = 0.899) and 10 years (6.8% vs. 9.9%; χ2 = 14.80, p = 0.676) of follow-up. The progression of microangiopathies was greater in the high vs. low for retinopathy (p = 0.008), diabetic kidney disease (p < 0.001), peripheral neuropathy (p = 0.021), and autonomic neuropathy (p = 0.008).
Conclusions: ST1RE performed well in predicting CV events at 5 and 10 years of follow-up. Moreover, higher ST1RE scores were associated with the progression of microangiopathy complications in this genetically heterogeneous T1D population.
Keywords: Cardiovascular risk; Chronic diabetes complications; Macrovascular disease; Microangiopathy; Steno Type 1 Risk Engine; Type 1 diabetes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Livingstone R, Boyle JG, Petrie JR. How tightly controlled do fluctuations in blood glucose levels need to be to reduce the risk of developing complications in people with type 1 diabetes? Diabet Med. 2019;37:513–21. - PubMed
-
- Soedamah-Muthu SS, Fuller JH, Mulnier HE, Raleigh VS, Lawrenson RA, Colhoun HM. High risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with type 1 diabetes in the U.K. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:798–804. - PubMed
-
- Miller RG, Anderson SJ, Costacou T, Sekikawa A, Orchard TJ. Hemoglobin A1c level and cardiovascular disease incidence in persons with type 1 diabetes: an application of joint modeling of longitudinal and time-to-event data in the Pittsburgh Epidemiology of Diabetes complications Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2018;187:1520–9. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

