Comparative brain metabolomics reveals shared and distinct metabolic alterations in Alzheimer's disease and progressive supranuclear palsy
- PMID: 39439201
- PMCID: PMC11667510
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14249
Comparative brain metabolomics reveals shared and distinct metabolic alterations in Alzheimer's disease and progressive supranuclear palsy
Abstract
Background: Metabolic dysregulation is a hallmark of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease (AD) and progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP). Although metabolic dysregulation is a common link between these two tauopathies, a comprehensive brain metabolic comparison of the diseases has not yet been performed.
Methods: We analyzed 342 postmortem brain samples from the Mayo Clinic Brain Bank and examined 658 metabolites in the cerebellar cortex and the temporal cortex between the two tauopathies.
Results: Our findings indicate that both diseases display oxidative stress associated with lipid metabolism, mitochondrial dysfunction linked to lysine metabolism, and an indication of tau-induced polyamine stress response. However, specific to AD, we detected glutathione-related neuroinflammation, deregulations of enzymes tied to purines, and cognitive deficits associated with vitamin B.
Discussion: Our findings underscore vast alterations in the brain's metabolome, illuminating shared neurodegenerative pathways and disease-specific traits in AD and PSP.
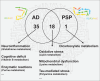
Highlights: First high-throughput metabolic comparison of Alzheimer's diesease (AD) versus progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) in brain tissue. Cerebellar cortex (CER) shows substantial AD-related metabolic changes, despite limited proteinopathy. AD impacts both CER and temporal cortex (TCX); PSP's changes are primarily in CER. AD and PSP share metabolic alterations despite major pathological differences.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; brain; cognitive deficit; metabolism; mitochondrial dysfunction; neuroinflammation; oxidative stress; progressive supranuclear palsy; tau‐mediated stress.
© 2024 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
R.K‐D., M.Arnold, G.K. are (through their institutions) inventors on key patents in the field of metabolomics, including applications for Alzheimer's disease. R.K‐D. holds equity in Metabolon Inc., a metabolomics technologies company. This platform was used in the current analyses. R.K‐D. formed Chymia LLC and PsyProtix, a Duke University biotechnology spinout aiming to transform the treatment of mental health disorders. M.Arnold and G.K. hold equity in Chymia LLC and IP in PsyProtix. J.K. holds equity in Chymia LLC, IP in PsyProtix, and equity in iollo. N.E.T. is an inventor on a patent through Mayo Clinic in PSP therapeutics. R.B., X.W., M.Allen, and C.B., have no conflicts. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures


Update of
-
Comparative brain metabolomics reveals shared and distinct metabolic alterations in Alzheimer's disease and progressive supranuclear palsy.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jul 27:2023.07.25.23293055. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.25.23293055. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Dec;20(12):8294-8307. doi: 10.1002/alz.14249. PMID: 37546878 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U19 AG074879/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30AG72975/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG003949/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG061359/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AARFD-22-974775/Alzheimer's Association award
- R01 AG017216/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072975/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG061796/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Sun Health Research Institute
- U01 AG046152/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1AG058942/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG025711/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1AG059093/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG46152/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research
- Arizona Alzheimers Research Center
- CurePSP Foundation
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30AG10161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG061356/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 4001/Arizona Biomedical Research Commission
- Mayo Foundation
- P30AG19610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG15819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NIH
- R01 AG069901/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072980/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 1001/Arizona Biomedical Research Commission
- U19 AG063744/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG061357/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 05-901/Arizona Biomedical Research Commission
- Alzheimer's Association Zenith Award
- R01 AG061796/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG032990/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS080820/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1U19AG063744/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG061359/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG006576/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- National Institute on Aging's Accelerating Medicines Partnership
- RF1 AG059093/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046139/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG061357/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 211002/Arizona Department of Health Services
- P01 AG003949/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 NS072026/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG17917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 0011/Arizona Biomedical Research Commission
- U01AG61356/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG025711/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19AG074879/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG017216/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01AG069901-01A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG058942/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Mayo Clinic
- R01 AG018023/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG006786/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

